how to check wifi hotspot in laptop cmd
Title: How to See WiFi Password using CMD
Channel: iShowCybersecurity
How to See WiFi Password using CMD by iShowCybersecurity
Unlock Your Laptop's WiFi Hotspot Secrets: The CMD Command You NEED!
Unveiling Your Laptop's Hidden WiFi Power: The CMD Command You Absolutely Must Know!
Ever wished you could share your laptop's internet connection effortlessly? Instead of fumbling with complicated software, there's a secret weapon right under your nose. You already possess it: the Command Prompt (CMD). Believe me, it's your gateway to WiFi hotspot liberation. It also offers a world of possibilities.
Ditching the Downloads: The CMD Advantage
We've all been there: the frustrating quest for the perfect hotspot software. Therefore, consider a shortcut! The CMD command eliminates needless downloads. Moreover, it simplifies the entire process. It's efficient, reliable, and remarkably effective. You are now in control of your hotspot setup.
Crafting Your Virtual Hotspot with Ease
Open the Command Prompt. You can find it by searching "cmd" in your Windows search bar. Right-click and select "Run as administrator". Next, the real magic begins.
Type and execute the following command: netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid="YourHotspotName" key="YourPassword"
Replace "YourHotspotName" with your desired hotspot name. Select a memorable one. Then, replace "YourPassword" with your secure password of your choice. Maintain strong password discipline. This is essential for preventing unauthorized access. After the command, hit Enter. You've just configured your virtual hotspot.
Starting Your WiFi Broadcast: One Command Away
Your hotspot is configured, but it's not active yet. To activate it, use this command in the CMD:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
Execute this promptly. Your laptop is now broadcasting WiFi. Other devices can connect. Consequently, your friends and family can now share your internet.
Troubleshooting Common Pitfalls: Smooth Sailing Ahead
Occasionally, things don't go as planned. Don't fret; most issues are easily resolved. If your hotspot isn't starting, verify a few things. First, ensure your wireless adapter is enabled. Second, check that you're connected to the internet. Third, and equally important, confirm your password. Ensure all commands are accurately typed. These precautions generally eliminate almost all initial problems.
Sharing Your Internet: A Seamless Experience
Now, to share the internet connection. Go to your Network Connections. You can find these by searching in the Windows search bar. Right-click the internet connection your laptop uses. Next, select "Properties". Click the "Sharing" tab. Finally, check the box that says "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection." Select your new hotspot. Click "OK". You've now successfully shared your internet.
Advanced Tweaks for the Savvy User
The CMD command offers flexibility. You can modify your settings later. To change the hotspot name or password, redo the initial configuration command. To disable the hotspot, use this command: netsh wlan stop hostednetwork. This shuts down the WiFi broadcast. You are in control of when it's active.
Security First: Protecting Your Connection
Security is paramount. Use a strong, unique password. Change your password regularly. Also, review connected devices periodically. This helps to maintain a safe and secure network. These practices protect your data from unwanted access.
Beyond the Basics: Expanding Your Knowledge
The CMD command is just the beginning. Explore further customization. Research other netsh wlan commands. Understanding these commands will boost your abilities. You'll become a WiFi hotspot expert.
Why This Method Reigns Supreme
Why CMD? Because it's readily available. It bypasses the hassle of third-party software. It is also a streamlined approach. It is efficient and reliable.
Embrace Your Laptop's Potential
You now possess the knowledge. You can create a WiFi hotspot. You can share your internet connection. Unlock your laptop's hidden potential. Enjoy the freedom and flexibility. Go forth and connect.
Laptop to WiFi Hotspot: The SHOCKINGLY Easy Trick You NEED to Know!Unlock Your Laptop's WiFi Hotspot Secrets: The CMD Command You NEED!
Hey tech adventurers! Ever found yourself stranded without Wi-Fi, staring longingly at your phone's data plan? Or maybe you've got a friend over, and their laptop is desperately begging for internet? We've all been there. But what if I told you there's a secret weapon, a hidden key, to unlock your laptop's potential as a Wi-Fi hotspot? Forget complicated software downloads and clunky user interfaces. Today, we're diving deep into a simple, yet powerful tool: the Command Prompt (CMD). And trust me, once you master this, you'll be the Wi-Fi wizard of your friend group.
1. So, What's the Big Deal About Turning Your Laptop into a Hotspot?
Think of your laptop as a digital Swiss Army knife. It’s got processing power, storage, and, with the right know-how, the ability to share its internet connection. This is where the hotspot magic comes in. It's absolutely crucial when you're traveling, in areas with spotty Wi-Fi, or just need to connect multiple devices. Imagine being stuck on a train with a dead zone but you've got a hefty data plan on your phone. Poof! Problem solved. It's all about convenience, connectivity, and saving those precious gigabytes. And let's be honest, showing off your tech skills to your less-tech-savvy friends is always a bonus, right?
2. The CMD Command: Your Secret Weapon
The Command Prompt – it sounds intimidating, I know. But really, it's just a window into your computer's soul. Think of it as a secret language your laptop understands. And the crucial command we need? It's your key to unlocking that Wi-Fi hotspot. We'll break it down step-by-step, so even if you're a complete beginner, you'll be setting up a hotspot like a pro.
3. Step-by-Step: How to Unleash the Hotspot Power
Okay, let’s get our hands a little dirty. Here’s the simple sequence you'll need to follow. Don't worry, it's easier than baking a microwaved pizza.
Open the Command Prompt: Click the Windows Start button, type "cmd," and select "Command Prompt" from the search results. Or, you can use the Windows key + R, type "cmd," and hit Enter. You'll get a black (or sometimes white) window.
The Magic Command: This is the bread and butter. Type in the following command and hit enter:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid="YourHotspotName" key="YourPassword"- Replace "YourHotspotName" with whatever you want to call your Wi-Fi (e.g., "AwesomeLaptop," "MyHotspot," etc.).
- Replace "YourPassword" with a strong password. Anything less than 8 characters is a bad idea, folks.
Start the Hotspot: Now, type this command and hit Enter:
netsh wlan start hostednetworkIf all goes well, you'll see a confirmation message. Congratulations, you've just created a Wi-Fi hotspot!
Share your Internet: Now, for the most common mistake people make. You need to share your internet connection. Here’s how:
- Click on the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray.
- Select "Network and Internet Settings."
- Click "Change adapter options."
- Right-click on the Wi-Fi adapter connected to your internet (generally, this is your actual Wi-Fi connection, not "Microsoft Hosted Network").
- Select "Properties."
- Go to the "Sharing" tab.
- Check the box that says, "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection."
- In the drop-down menu, select "Microsoft Hosted Network Virtual Adapter."
- Click "OK."
Troubleshooting (because things aren't always perfect): Sometimes, things don't go smoothly. Don’t worry, it happens to the best of us. We’ll cover some common issues later.
4. Customizing Your Hotspot: Name, Password, and Security
You're not just stuck with a generic hotspot; customize away!
- The SSID (Service Set Identifier): This is the name of your Wi-Fi network. Choose something memorable. Or, you know, be funny.
- Password Security: Always use a strong password! This is your shield against unwanted users piggybacking on your internet. Think of it as a lock on your digital house.
- Security Type: While the CMD command doesn't explicitly specify a security type, it defaults to using WPA2-PSK. This is generally secure for home use.
5. Why This CMD Method Beats the Alternatives
Why bother with this command-line stuff when there are apps and settings menus, you ask? Well, a few reasons!
- Simplicity: It's faster and more direct than navigating through complicated menus.
- Lightweight: Doesn't require installing extra software, saving space and system resources.
- Reliability: Often more stable since it uses built-in Windows features.
- Control: Gives you precise control over your hotspot settings.
6. Potential Pitfalls and How to Dodge Them
Let's talk about potential issues. Here's a rundown of what might trip you up, and how to get back on track.
- "The hosted network couldn't be started" error: This can be due to various problems. First, double-check you typed the command correctly. Next, ensure your Wi-Fi adapter drivers are updated. Finally, verify that the "Microsoft Hosted Network Virtual Adapter" is enabled in your Network Connections (accessed via
ncpa.cplin the Run dialog). - Internet Sharing Issues: This is a common one! Ensure the "Allow other network users…" box is checked under the sharing settings of your primary internet connection, as we discussed earlier. Make sure the correct adapter is selected. Restarting the hosted network after changing this can help too.
- Driver Problems: Outdated or corrupted Wi-Fi drivers can cause glitches. Update them through Device Manager.
- Firewall Interference: Your firewall might be blocking the hotspot. Temporarily disable it to see if it solves the problem. If it does, you'll need to create a rule to allow the hosted network.
7. Troubleshooting 101: Conquering Common Challenges
Let's get down to some real-world troubleshooting scenarios you're likely to face. Here’s how to deal with them:
- The Hotspot Won't Connect: Double check the password. Make sure the host network is started, and is enabled for sharing. Try restarting your computer.
- Slow Speeds: This depends entirely on your internet speed. Is it slow on your laptop too? If so, your hotspot will be slow. Also, the more devices connected, the slower it gets.
- "Cannot find wireless adapter" Error: This means your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter either isn't enabled, is malfunctioning, or the drivers need to be updated. Check Device Manager to diagnose.
8. Your Laptop's Virtual Router: More Than Just a Hotspot
This isn't just about sharing internet; it's about understanding how your laptop can transform into a mini-router. Consider this a gateway to:
- Testing Your Devices: Need to make sure your phone, tablet, or smart TV can connect to a Wi-Fi network? Use your laptop as a temporary testbed.
- Extending Your Network: Need to cover a larger area than your main router? Your laptop can act as a signal booster.
- Creating a Secure Environment: When traveling or using public Wi-Fi, using your laptop as a hotspot can give you a more secure connection for your other devices.
9. The Impact of the CMD Hotspot on Data Usage
Be mindful of your data usage! If you're using a limited data plan, the data consumed by devices connected to your hotspot will come directly from your laptop's internet connection. Monitor your data usage closely, especially with activities like streaming or downloading large files. Consider setting data limits on your phone to control consumption.
10. Power Consumption and Hotspot Longevity
Running a hotspot can drain your laptop's battery, like running a marathon. Be aware of this.
- Battery Life Savers: Plug in your laptop whenever possible.
- Optimize Power Settings: Adjust your power plan to maximize battery efficiency.
- Limit Connected Devices: Fewer devices = less drain.
11. Safety First: Security Best Practices
While we're on the subject of security, let's reinforce a few points:
- Strong Passwords: Absolutely critical. Don’t use anything predictable.
- Firewall: Keep your firewall enabled.
- Regular Updates: Keep your operating system and drivers updated to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor Connected Devices: Keep an eye on devices connected to your hosted network and kick off any unknown
How to Know Wifi Password With CMD Buat Kamu Lupa Password Wifinya yaa.....
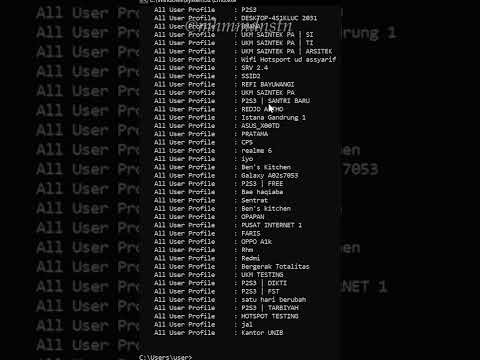
By HaiNasta How to Know Wifi Password With CMD Buat Kamu Lupa Password Wifinya yaa..... by HaiNasta
Check WiFi Password Using cmd viral trending itinhindi shorts shortvideo

By IT in Hindi Check WiFi Password Using cmd viral trending itinhindi shorts shortvideo by IT in Hindi
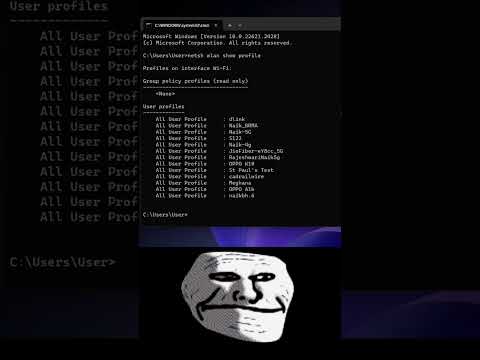
Title: How to check wifi password using cmd shortsfeed cmdtricks
Channel: Futurify Lab
How to check wifi password using cmd shortsfeed cmdtricks by Futurify Lab
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
Unlock Your Laptop's WiFi Hotspot Secrets: The CMD Command You NEED!
The modern digital landscape demands seamless connectivity, a reality that often hinges on the availability of reliable Wi-Fi. Yet, what happens when a traditional router isn't within reach, or when you need to share a crucial internet connection with devices that lack direct access? The answer, often overlooked, lies within the potent capabilities of your very own laptop, specifically through the power of a simple yet transformative Command Prompt (CMD) command. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the fascinating world of turning your laptop into a fully functional Wi-Fi hotspot, liberating you from connectivity constraints and allowing you to share your internet connection with ease.
Understanding the Core Concept: Software-Defined Wi-Fi
At the heart of creating a laptop-based Wi-Fi hotspot lies the principle of software-defined networking. Essentially, your laptop's built-in Wi-Fi adapter, traditionally used for receiving Wi-Fi signals, can be repurposed to transmit a Wi-Fi signal. This remarkable feat is achieved through software, specifically the operating system's built-in networking tools. By activating a hidden feature within Windows, you can essentially "split" your existing internet connection and broadcast it as a separate Wi-Fi network, allowing other devices to connect and share your internet access. Think of it like a mini-router, but built entirely within your laptop.
The Gateway to Connectivity: The netsh wlan Command
The command itself is the key. Within the Command Prompt, the netsh wlan command package is the instrument that will allow you to make the magic happen. This command, part of the broader Windows networking (Netsh) utility, offers a rich set of functionalities, including the management of wireless network interfaces. With this one command, the world opens up to you. Let's break down the process:
Step 1: Launching the Command Prompt With Elevated Privileges
This step is crucial. The CMD commands we'll use manipulate network settings that are restricted without administrator access. You must open the Command Prompt with elevated privileges for these steps to work:
- Click the Windows Start button.
- Type "cmd" into the search bar. Do not just press enter.
- Right-click on "Command Prompt" in the search results.
- Select "Run as administrator."
- If prompted by User Account Control (UAC), select "Yes" to grant administrative privileges. Your screen may look different depending on the version of Windows.
Step 2: Preparing for Deployment: Creating the Hosted Network
This is where the magic begins. We'll utilize the netsh wlan set hostednetwork command to configure the virtual Wi-Fi hotspot.
In the Command Prompt, type the following command and press Enter:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid="YourHotspotName" key="YourPassword"Replace
"YourHotspotName"with the name you want to assign to your hotspot (e.g., "MyLaptopHotspot"). Replace"YourPassword"with a strong, secure password (at least eight characters long) that you will use to protect your Wi-Fi network. Make sure to choose a password that is not easy to guess. Passwords should be a combination of numbers, letters, and symbols.mode=allow: This parameter enables the hosted network.ssid="YourHotspotName": This parameter specifies the Service Set Identifier (SSID), the name that will be broadcast to your devices, which is what will show up on the list of available Wi-Fi networks.key="YourPassword": This parameter sets the security key (password) for your hotspot. Without the correct password, people cannot connect to your Wi-Fi hotspot.
Step 3: Activating the Hotspot: Starting the Hosted Network
Now that the hotspot is configured, it is time to activate it to make it available to others. Enter the following command and press Enter:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
This command does exactly what it says: it starts the hosted network, meaning your laptop will begin broadcasting its Wi-Fi signal, and other devices, given the correct password you set in step 2, will be able to connect.
Step 4: Sharing Your Internet Connection (Crucial!)
The hotspot is now broadcasting, but it's not yet sharing your internet. You have to configure your primary network connection to allow sharing; the connection may be Ethernet or Wi-Fi. Without doing this, the hotspot will exist, but your devices will not have internet connectivity. To achieve this:
- Open the Network Connections panel. You can do this by typing "Network Connections" in the Windows search bar and selecting the appropriate result.
- Locate the network adapter that currently provides your internet connection (e.g., your Wi-Fi adapter if you're connected to Wi-Fi or your Ethernet adapter if you're connected via an Ethernet cable). The adapter that is connected to the internet.
- Right-click on your primary connection and select "Properties."
- Go to the "Sharing" tab.
- Check the box that says "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's internet connection."
- In the "Home networking connection" dropdown, select "Microsoft Hosted Network Virtual Adapter" or the name that is similar.
- Click "OK."
This action will then enable your computer to share the existing internet connection through the virtual, hosted network.
Step 5: Connecting Your Devices
With the hotspot activated and internet sharing enabled, it is now possible for other devices to connect.
- On your devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops, etc.), open the Wi-Fi settings.
- Search for available Wi-Fi networks. Your hotspot name ("YourHotspotName" as configured in Step 2) should appear on the list.
- Select your hotspot name.
- Enter the password you created.
- The device should then connect to your laptop's Wi-Fi hotspot and gain internet access.
Step 6: Disabling the Hosted Network
To turn off your Wi-Fi hotspot, follow these steps:
Open the Command Prompt as administrator (follow instructions in Step 1).
Type and enter the following command:
netsh wlan stop hostednetwork
This will no longer broadcast the hotspot.
Step 7: Stopping the Hosted Network
To completely remove the hotspot settings, follow these steps:
Open the Command Prompt as administrator (follow instructions in Step 1).
Type and enter the following command:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=disallow
This prevents you from accidentally starting it again.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While the process is generally straightforward, you may encounter some issues. Here's how to address them:
- "Hosted network could not be started" error: Ensure you are running the Command Prompt as an administrator. Verify that your Wi-Fi adapter supports hosted network functionality. Driver updates are also important, so make sure your drivers are up to date.
- Devices connect but have no internet access: Verify that you have enabled internet connection sharing as described in step 4. Troubleshoot your primary internet connection on the laptop. Check that the firewall is not blocking the connection – temporarily disabling the firewall can help to test this (but re-enable it afterward for security).
- Slow speeds: The laptop is essentially re-broadcasting a signal and is sometimes slower than a dedicated router. The speed will depend on your primary connection and how many devices are using the hotspot. If speeds are poor, try to reduce the distance between your laptop and the devices and make sure you have a strong internet connection. Restarting your laptop and internet connection are also helpful.
- "The wireless network adapter does not support the requested operation": In this situation, ensure your Wi-Fi adapter drivers are up to date and that your physical adapter supports hosted networks. Some older or more basic Wi-Fi adapters may not have the necessary functionality. You may need to replace the Wi-Fi adapter or connect an external USB Wi-Fi adapter.
Beyond the Basics: Customization and Optimization
Once you have the basics mastered, you can further customize and optimize your hotspot experience.
- Changing the network name and password: You can modify your network name (SSID) and password at any time using the
netsh wlan set hostednetworkcommand followed bymode=allow, as described back in step 2. - Monitoring Connected Devices: While the
netsh wlancommand does not directly provide a list of connected devices, you can use network monitoring tools to keep an eye on who is using your hotspot and potentially block unwanted connections. - Prioritizing Bandwidth: If you have multiple devices connected to your hotspot, consider using Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your laptop to prioritize bandwidth for specific applications or devices, ensuring a smoother experience. This is an advanced topic and requires more technical knowledge.
- Security Best Practices: Always use a strong, unique password for your hotspot. Avoid using easily guessable passwords or personal information. Regularly change your password to increase network security. Consider enabling WPA2 or WPA3 encryption for the most secure connection.

