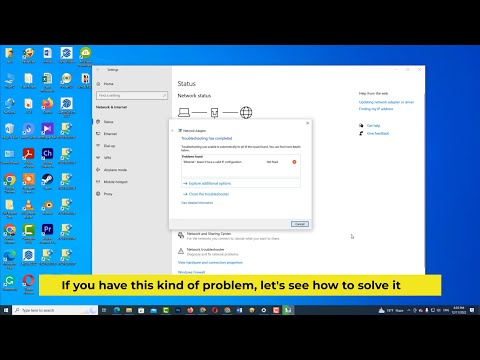
ethernet doesn't have a valid ip configuration laptop wifi share
Title: Fix ethernet doesn't have a valid ip configuration issue in windows 10 Windows 11
Channel: IT Magics
Fix ethernet doesn't have a valid ip configuration issue in windows 10 Windows 11 by IT Magics
Laptop WiFi Sharing Nightmare? FIX Ethernet's IP Address NOW!
Solve Your Laptop's WiFi Sharing Woes: A Simple Ethernet IP Address Fix!
Have you ever felt utterly defeated by your laptop's inability to share its internet connection? It's a common frustration. It's especially irritating when you're trying to connect multiple devices. You know the issue: your laptop's WiFi seems to be working fine. However, when you try to share that connection via Ethernet, nothing works. Sound familiar? You're not alone. Many people experience this exact problem. Fortunately, there's a straightforward solution.
The Ethernet IP Address Conundrum: Decoding the Problem
The root cause of this technical headache often boils down to your Ethernet's IP address. Now, don't panic! You don't need a degree in computer science to understand this. In essence, your Ethernet connection needs a specific IP address. It needs it to communicate properly with other devices. Furthermore, your laptop's operating system might be assigning an incorrect or conflicting address. So, the shared internet connection fails. But, the good news is: it’s usually easy to fix. You've reached the right place. We’ll explore the solution step-by-step.
Step-by-Step: Fixing Your Ethernet IP Address for Seamless Sharing
First, you’ll need to access your network settings. It’s the control center for all things internet related. Therefore, locate your network connections. Then, find the Ethernet adapter within those settings. Now, follow these simple steps:
Accessing Your Network Adapter Settings: Navigate to your control panel. You may also right-click on the network icon in your system tray. Select "Open Network and Internet settings." Next, go to "Change adapter options." This will show all your network adapters. These will include Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and any virtual adapters.
Identifying Your Ethernet Adapter: In that list, locate your Ethernet adapter. It’s generally labeled something like "Ethernet" or "Local Area Connection." The name may vary depending on your specific setup.
Accessing IPv4 Properties: Right-click on your Ethernet adapter icon. Then, choose "Properties." A properties window will appear. Within this window, look for "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)." Select it and click "Properties." This section is crucial.
Setting a Static IP Address (the Magic Touch): Here’s where the magic happens. Switch from "Obtain an IP address automatically" to "Use the following IP address." This gives you manual control.
Choosing an IP Address: Now, for the IP address itself. This can feel intimidating. However, it’s actually relatively simple. Consider using 192.168.1.X, where X is a number between 2 and 254. Most home networks use this range. For example, you could use 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.15, or any other number within that range, as long as it is unique on your network.
Subnet Mask and Gateway: Enter the subnet mask. It’s usually 255.255.255.0. Also, input your gateway address. This is often the same as your router’s IP address. The gateway is often 192.168.1.1. Check your router's documentation if unsure.
DNS Server Configuration: Below the IP address settings, input your preferred DNS servers. The DNS translates domain names into IP addresses. You can use your internet service provider's DNS servers. You can also use public DNS servers like Google (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
Finalizing the Changes: Click "OK" to close the IPv4 properties window. Then, click "OK" again to close the Ethernet adapter properties window. Your changes are now saved.
Troubleshooting and Refinement: Fine-Tuning the Connection
It's possible, despite following these steps, that the problem persists. Rest assured, troubleshooting is straightforward. Restart your laptop. After that, also restart the device you are trying to connect. Now, test the internet connection again. If it still doesn’t work, double-check all the settings. Make sure you entered everything correctly. Another potential issue could be your firewall. Ensure it's not blocking the connection. Temporarily disable the firewall to see if that resolves the issue.
Beyond the Basics: Further Enhancements and Considerations
Once the Ethernet IP address configuration is resolved, explore further possibilities. Consider using a network cable with a good quality. Cheap cables can sometimes cause problems. Also, consider updating your network adapter drivers. Outdated drivers could cause compatibility issues. Check your laptop manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers. Finally, always ensure your router's firmware is updated, too. This improves performance and security.
The Takeaway: Enjoy Seamless Internet Sharing!
In conclusion, fixing your Ethernet IP address is often the key to unlocking seamless internet sharing. The steps outlined above provide a simple, effective solution. You now have the knowledge to combat frustrating connectivity issues. By following these easy steps, you can transform your laptop. You can transform it into a reliable internet sharing hub. So, you can enjoy a smooth, hassle-free experience. Share the joy with others. Say goodbye to WiFi sharing nightmares! Enjoy a reliable internet connection.
Unlock Your Laptop's Hidden Hotspot: Free WiFi Anywhere!Laptop WiFi Sharing Nightmare? FIX Ethernet's IP Address NOW!
Ever tried sharing your laptop's Wi-Fi and felt like you were navigating a digital Bermuda Triangle? You connect, you share, and then… nothing. The other device stares blankly at you, the dreaded "no internet access" message mocking your tech prowess. Trust me, we've all been there. Picture this: you're in a vital meeting, on a road trip, or just trying to stream your favorite show. The Wi-Fi connection is spotty or nonexistent, and you desperately need to share your laptop's precious internet lifeline. That's when the frustration mounts, and the search for a solution begins. This is where understanding your Ethernet's IP address and how it dances with your Wi-Fi sharing setup becomes critical! We're peeling back the layers of this digital onion and offering you a definitive fix. Let's get started!
1. The Wi-Fi Sharing Saga: A Tale of Two Networks
Think of your laptop as a bridge. On one side, you have your Wi-Fi, connecting you to the vast expanse of the internet. On the other, you have Ethernet, the often-forgotten sibling that connects to other devices, usually via a cable. When you try to share Wi-Fi, your laptop attempts to act as the middleman, routing internet traffic from your Wi-Fi connection to whatever device you're trying to share with. The problem? Sometimes, these two networks get confused, like siblings squabbling over who gets the best toy. The key to resolving this clash often lies in ensuring your Ethernet connection is correctly configured.
2. Why Ethernet Matters (Even If You're Mostly Wireless)
Many of us are wireless warriors these days. We embrace the freedom of Wi-Fi. However, the truth is, your laptop's Ethernet port is still an essential piece of the puzzle, especially if you intend to share your Wi-Fi. Consider Ethernet as the silent, reliable workhorse. It's your connection point to other devices when you're sharing your precious internet. And like any workhorse, it needs to be in top shape.
3. The IP Address: Your Digital Passport
Your IP (Internet Protocol) address is like your digital passport; it's how devices identify themselves on a network. Every connection needs one! When sharing Wi-Fi, you’re essentially telling your laptop, "Hey, share my internet connection using Ethernet." Your laptop then assigns an IP address to the device using Ethernet. However, sometimes your laptop gets a bit confused by the IP configuration and assigns an IP that disrupts the process. This is precisely what leads to that dreaded "no internet access" error.
4. Unmasking the Culprit: Finding Your Ethernet IP Address
Before we dive into the fix, we need to know what’s broken. Finding your Ethernet IP address is easier than you think. Here’s how we'll do it on Windows:
- Windows: Open the "Settings" app (the gear icon). Navigate to "Network & Internet" > "Ethernet." Click on the name of your Ethernet connection. Scroll down to find your "IP address" listed under IPv4 address.
Pro Tip: In the settings, we can usually discover that your Ethernet IP address is likely assigned automatically. This is the source of your trouble, and we're about to fix it!
5. The Big Fix: Assigning a Static IP Address
The most reliable solution is assigning a static IP address to your Ethernet connection. This tells the system, "Always use this address." We'll guide you step-by-step:
- Back to Ethernet Settings: Return to the Ethernet connection settings (see step 4).
- Edit IP Assignment: Click "Edit" next to "IP assignment." Change it from "Automatic (DHCP)" to "Manual."
- Switch On IPv4: Switch on IPv4 to enable manual IP configuration.
- Input Your Static IP: You’ll need a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Here’s how to get these values:
- IP Address: Choose an IP address within your network's range but not in use. An example could be, 192.168.1.100. Ensure that it’s not the same as the IP address of your devices on the network.
- Subnet Mask: Type in 255.255.255.0 (usually the default)
- Default Gateway: Enter the IP address of your router (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, but check your router's documentation)
- DNS Servers: Enter your preferred DNS server addresses (e.g., Google's: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4, or Cloudflare's: 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
- Save the Changes: Click "Save."
6. Connecting the Dots: Sharing Your Internet
With your Ethernet IP address fixed, sharing becomes a breeze. Here's how to do it on a Win box:
- Network and Sharing Center: (Search in your Start menu, and find "Network and Sharing Center" or "View Network Connections.")
- Change adapter settings: Click on "Change adapter settings."
- Right-click Wi-Fi: Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Properties: Select "Properties."
- Sharing Tab: Go to the "Sharing" tab.
- Allow Sharing: Check the box that says, "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection."
- Select Ethernet: In the dropdown menu, select your Ethernet connection.
- Share! Click "OK"
7. Testing the Waters: Is It Working?
Connect the device you were initially trying to share your Wi-Fi connection with to your laptop using an Ethernet cable, and test the internet access. Did it work? If so, you've successfully conquered the Wi-Fi sharing nightmare! If not, go through the steps again, paying strict attention to the details.
8. Troubleshoot: When Things Go Wrong
Sometimes, even with the best intentions, things can go sideways. Here are a few common issues and their solutions:
- Incorrect IP Address: Double-check the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. Make sure they are correct.
- Network Conflicts: Ensure no other devices on your network are using the same static IP address.
- Firewall Issues: Your firewall might be blocking the connection. Temporarily disable it to test. Be sure to re-enable it afterward when using it.
- Driver Problems: Ensure that your Ethernet adapter drivers are up-to-date. Go to Device Manager to verify.
9. Beyond the Basics: Advanced configurations
- Multiple Devices: If you have multiple devices to connect, you might need an Ethernet switch to expand the number of ports.
- Network Bridge: For a more advanced setup, you can create a network bridge; although this is generally unnecessary for simple Wi-Fi sharing.
10. The Power of Patience: A Lesson in Tech
Troubleshooting tech issues is like assembling IKEA furniture: It can be frustrating, but with patience and attention to detail, you will succeed. Don’t get discouraged!
11. Why Static IP? The Advantages
The beauty of a static IP is its reliability. It ensures the Ethernet connection always uses the same IP address, eliminating the dynamic re-assignment that often causes conflicts.
12. Comparing Configurations: Automatic vs. Static
Choosing between automatic (DHCP) and static IP assignment boils down to your needs. Static is king for shared connections, whereas automatic is convenient for basic, single-device usage.
13. Sharing and Security: A Delicate Balance
When sharing your Wi-Fi, it’s crucial to be aware of security. Ensure your Wi-Fi network is secured with a strong password.
14. The Ripple Effect: How IP Affects All Connections
Remember, your IP address impacts all your network connections, not just Wi-Fi sharing. It's fundamental, affecting everything from browsing to gaming.
15. Embrace the Knowledge: You Are Now the Expert!
You now have the knowledge. You are armed with knowledge to troubleshoot and fix Wi-Fi sharing problems. Go forth and connect, share, and conquer.
Closing Section
The Wi-Fi sharing experience is often a source of frustration, leaving us scrambling for solutions when we need connectivity the most. By taking a deep dive into your Ethernet's IP settings, you unlock the power to share your internet reliably. We've provided a detailed guide, from understanding IP addresses to assigning a static IP, empowering you to overcome the common hurdles. The next time you find yourself in a Wi-Fi sharing crisis, remember this guide. You are now equipped to handle the challenge confidently. Embrace the knowledge, and transform those sharing nightmares into seamless, connected experiences.
FAQs
1. What if my device still can’t connect after I set a static IP?
- Double-check all your settings (IP address, subnet mask, gateway, DNS). Ensure your
How to Fix Ethernet Doesn't Have a valid IP Configuration

By TechSimplify How to Fix Ethernet Doesn't Have a valid IP Configuration by TechSimplify
WiFi Doesn't have a valid IP configuration on Windows 10

By FIXsage WiFi Doesn't have a valid IP configuration on Windows 10 by FIXsage
Cara Mengatasi Wifi Tidak Konek Internet - wifi2 doesnt have a valid ip configuration
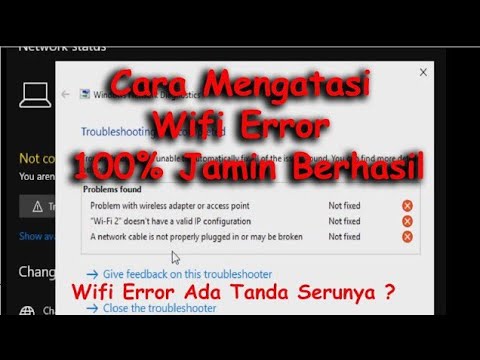
By TRAR Cara Mengatasi Wifi Tidak Konek Internet - wifi2 doesnt have a valid ip configuration by TRAR

Title: How to Fix Wi-fi Doesnt Have A Valid IP Configuration
Channel: TechSimplify
How to Fix Wi-fi Doesnt Have A Valid IP Configuration by TechSimplify
Wifi On Laptop Phone
Laptop WiFi Sharing Nightmare? FIX Ethernet's IP Address NOW!
We've all been there, haven't we? The promise of seamless internet connectivity, the expectation of a smooth workflow, utterly shattered by the dreaded "no internet" error message, right when you need it most. You’re trying to share your laptop's Wi-Fi connection via Ethernet, perhaps to provide internet to a gaming console, another PC, or a smart TV, and the connection just won’t cooperate. The frustration mounts, the deadlines loom, and the search for a solution begins. Often, the source of this technological tempest lies, surprisingly, within the seemingly innocuous realm of your laptop's Ethernet connection and, specifically, its IP address configuration. This seemingly small detail can be the key that unlocks a world of connectivity, or the lock that slams the door shut on your online ambitions. Let’s dive in and untangle this perplexing issue. You might be surprised at how straightforward the solution can be.
Understanding the Ethernet-WiFi Bridge
Before we delve into the fix, let's briefly clarify the basic mechanisms. When you're trying to share your laptop's Wi-Fi connection through the Ethernet port, you're essentially creating a mini-network. Your laptop acts as a bridge, taking the wireless connection it receives and distributing it through the physical Ethernet cable. This process relies on proper communication between your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter and its Ethernet adapter. Often, the problem boils down to how these two adapters are configured to exchange data, with the Ethernet adapter's IP address being the primary culprit.
The Root of the Problem: Conflicting or Incorrect IP Addresses
The most common cause of this Wi-Fi sharing failure is a conflict or a misconfiguration of the Ethernet port's IP address. Think of it like this: your Ethernet port needs a unique "address" to communicate with the devices you are connecting to it. This address is the IP address.
Automatic IP Allocation (DHCP): By default, most devices are set to obtain an IP address automatically, using a protocol called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Your router usually provides this, giving each device a seemingly random, unique IP address. If your laptop's Ethernet adapter also tries to get an address automatically, it’s likely that the system will assign it an address in a range that conflicts with your primary network. Thus, it wouldn’t be able to properly forward internet traffic. While a router will usually prevent this, it does sometimes happen.
Static IP Addresses: On the other hand, a static IP address, manually configured, can also cause problems. If the IP address you've assigned to your Ethernet adapter is incorrect, or if it conflicts with an existing device on your network, the connection will fail.
Step-by-Step: Fixing the Ethernet IP Address
Now, let's get to the core of the solution. Here's a step-by-step guide to diagnose and resolve the IP address issue on your laptop's Ethernet adapter:
Accessing Network Settings: First, you need to access your network settings. On Windows:
- Right-click on the network icon in your system tray (usually located in the bottom-right corner of your screen).
- Select "Open Network & Internet settings."
- Click on "Change adapter options." This will open a window displaying all your network adapters.
On macOS:
- Click the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen.
- Select "System Preferences."
- Click on "Network."
Identifying Your Ethernet Adapter: In the "Network Connections" window (Windows) or the "Network" preferences (macOS), you will see the list of your network adapters. Identify the one labeled "Ethernet" (it may also be labeled "Local Area Connection" on Windows). Make sure your Ethernet cable is plugged in to your computer.
Accessing Ethernet Adapter Properties: Right-click the "Ethernet" adapter and select "Properties" (Windows) or select your Ethernet adapter, and click "Advanced" then "TCP/IP" (macOS). This will open a new window.
IP Address Configuration: This is where the magic happens. In the Properties window (Windows), find "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)". Select it and then click "Properties" (Windows). On macOS, this will be displayed in the "Configure IPV4" dropdown.
Choosing the Right IP Configuration: Here, you’ll be tweaking the IP settings. Here are the two most common configurations, along with guidance on which will work best:
Option A: Automatic IP Address (DHCP): This is the simplest and, in many cases, the best option. Select "Obtain an IP address automatically" (Windows) or "Using DHCP" from the Configure IPv4 dropdown (macOS). This tells your Ethernet adapter to automatically request an IP address from your router or the device you’re connecting to. After making this change, click "OK" to save the settings and close the windows.
- In most home networks, this setting will work seamlessly.
- If you are using a specific network, a gaming console, or a smart TV and experiencing issues, try the next option.
Option B: Manual Configuration (Static IP Address): This option is for you if you have specific network needs or if the automatic configuration doesn’t work effectively. Here, you will assign a static IP address. However, this can be tricky, so make sure you have the appropriate information. Select "Use the following IP address" (Windows) or "Manually" from the Configure IPv4 dropdown (macOS).
- IP Address: You'll need to enter an IP address that is not already in use on your network. To avoid conflicts, you should look at your router's settings. You can usually access the router's admin panel using a web browser and the router's IP address (often something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Look for a list of connected devices and their IP addresses. Then, pick an IP address that is outside of the range your router is assigning automatically. A popular choice for your Ethernet adapter is within the range of 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.199, as your DHCP often uses the range of 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99. Remember, you must be within the same subnet, so the first three numbers of the IP address (e.g., 192.168.1) must match the router's network.
- Subnet Mask: This is usually 255.255.255.0.
- Default Gateway: This is the IP address of your router (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- DNS Servers: You can use your router’s IP address as the primary DNS server. Alternatively, you can use public DNS servers like Google's (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare's (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
Restart Your Laptop and Test: After making any changes to the IP settings, you must restart your laptop. Close all the windows and restart your machine. This ensures that the new settings fully take effect. Once your laptop restarts, connect your Ethernet cable and test the connection. Check for internet access on the devices connected through the Ethernet cable, and also on your laptop's Wi-Fi to ensure the internet is still available.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after following these steps, you may still encounter some roadblocks. Let's address a few common troubleshooting scenarios:
- "Limited" or "No Internet Access": This usually indicates a problem with the IP address configuration. Double-check the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway settings. Ensure that the IP address is within the correct range for your network and that it's not a duplicate.
- "Identifying…" for an Extended Period: This can point to a problem with DHCP. Try renewing your IP address: open a command prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS) and type
ipconfig /renew(Windows) orsudo ifconfig en0 down; sudo ifconfig en0 up(macOS) followed byipconfigorifconfigto see the IP address that was assigned. This will attempt to reacquire an IP address from your router. On macOS, replace en0 with the correct number for your ethernet adapter. - Router Issues: Sometimes, the issue isn't with your laptop but with your router. Try restarting your router. Also, make sure your router's firmware is up-to-date. Outdated firmware can cause various connectivity problems.
Advanced Considerations: Network Bridging and Internet Connection Sharing
For advanced cases or if the simple fixes aren't working, Windows and macOS offer built-in tools for network bridging and internet connection sharing. These features automate the process of sharing your internet connection.
Windows Internet Connection Sharing:
- Go to "Network Connections" (as described above
