wifi driver windows 7 hp laptop

Title: Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011
Channel: inprez id
Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011 by inprez id
wifi driver windows 7 hp laptop, wifi driver for windows 7 hp laptop download, internet driver for windows 7 hp laptop, wifi driver windows 7 32 bit for hp laptop, realtek wifi driver for windows 7 hp laptop, wifi driver for windows 7 hp 2000 laptop, wifi driver for windows 7 64 bit hp laptop free download, wifi driver for windows 7 32 bit hp laptop free download, free download wifi driver for windows 7 hp laptop, how to install wifi driver in windows 7 hp laptop
HP Laptop Wifi Nightmare? Fix Your Windows 7 Connection NOW!
HP Laptop Wi-Fi Woes? Conquer Your Windows 7 Connection Today!
Is your HP laptop throwing a Wi-Fi tantrum? Are you facing the dreaded "no connection" message? Don't fret! It can feel frustrating to have your online access cut off. However, you're not alone. Many HP Windows 7 users encounter Wi-Fi issues. Fortunately, fixing these problems is usually straightforward. So, let’s get your laptop back online, fast!
Unearthing the Culprit: Common Wi-Fi Connection Killers
First, we need to diagnose the issue. Several factors could be sabotaging your wireless connection. Therefore, consider these usual suspects:
- The Router's Role: Your router is the gateway to the internet. Is it functioning correctly? Sometimes, a simple reboot works wonders. Unplug your router and modem. Wait a minute or two, then plug them back in. After that, wait for them to fully restart.
- Driver Dilemmas: Outdated or corrupted Wi-Fi drivers are a frequent cause. These are the software packages that enable your laptop's wireless adapter to communicate.
- Misconfigured Settings: Incorrect network settings can block your access. It's easy to accidentally change something. This can disrupt your connection.
- Hardware Hurdles: Occasionally, the Wi-Fi adapter itself is faulty. This is less common, however. But, it’s worth considering.
Driver Detective: Updating and Troubleshooting
Moreover, let's tackle the issue of drivers. They are the heart of your Wi-Fi adapter. The good news is, updating your drivers is usually a simple fix. Here's how:
- Open Device Manager: Go to your Start menu. Then, type "Device Manager" in the search bar and select it.
- Locate Network Adapters: In Device Manager, find "Network adapters." Click the arrow to expand the list.
- Right-Click and Update: Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter (it might be labeled something like "Wireless Network Adapter"). Select "Update driver."
- Automatic Search: Choose "Search automatically for driver software." Windows will search for, download, and install the latest driver.
- Restart and Retry: After restarting your computer, test your Wi-Fi connection. Hopefully, it works now!
In case the automatic update fails, you could visit the HP website. There, search for drivers specific to your laptop model. Download and install the latest Wi-Fi driver version.
Network Troubleshooter: A Built-In Ally
Meanwhile, Windows 7 has a built-in network troubleshooter. It’s a handy tool that can automatically diagnose and fix common network issues. To run it:
- Access Network and Sharing Center: Click the network icon in your system tray (usually in the bottom right corner). Then, select "Open Network and Sharing Center."
- Troubleshooting: Click "Troubleshoot problems." Windows will begin to diagnose any connection issues.
- Follow Suggestions: The troubleshooter will provide suggested fixes. Apply them.
Power Saving Pitfalls: Disabling the Power Saver
Windows 7 may have set up power-saving options. Unfortunately, these can sometimes interfere with Wi-Fi connectivity. For now, temporarily disable this feature.
- Device Manager Again: Go back to Device Manager. Find your Wi-Fi adapter again.
- Properties: Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter. Choose "Properties."
- Power Management: Navigate to the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the Box: Uncheck the box labeled "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- Apply and Test: Click "OK." Restart your laptop. Then, test your connection.
Static vs. Dynamic IP: Configuration Check
After that, let's look at IP settings. It is possible your IP address is not set up correctly. Therefore, you should examine your network configuration. Make sure your settings are properly enabled.
- Open Network Connections: Go to the Start menu. Then, type "ncpa.cpl" in the search bar and press Enter.
- Adapter Properties: Right-click your wireless network connection. Select "Properties."
- TCP/IP v4: Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" from the list. Then, click "Properties."
- Obtain Automatically: Ensure "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected. If not, select these options.
- Apply and Reboot: Click "OK" on both windows. Restart your computer and try connecting again.
Security Settings: Password Protection and More
Furthermore, incorrect security settings on your router might be causing issues. Ensure your Wi-Fi password is correct. Then, double-check that your security protocol is supported by your laptop.
- Access Router Settings: Enter your router's IP address into your browser. The default address is usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Consult your router's manual if unsure.
- Login: You'll need your router's username and password. Check the manual.
- Wireless Settings: Find the "Wireless" or "Wi-Fi" settings.
- Security Configuration: Verify the security type (WPA2 is recommended) and password.
- Save and Retest: Save the settings. Then, reconnect your laptop.
Hardware Assessment: When All Else Fails
Finally, if all else fails, consider a potential hardware problem. This is less probable, but it can happen.
- Internal Checks: First, ensure your Wi-Fi adapter is enabled in your laptop’s BIOS settings. Access often involves pressing a key like F2 or Delete during startup.
- External Adapter: As a last resort, an external USB Wi-Fi adapter is an option. This bypasses your internal adapter.
Victory! Reclaiming Your Wi-Fi Connection!
By following these steps, you should be able to resolve your HP laptop's Wi-Fi issues. Remember to restart your computer after making changes. With some persistence, you'll soon be back online. Now, you can enjoy seamless wireless internet connectivity. Happy surfing!
Unlock iPhone WiFi on Your Laptop: The Secret Trick No One Tells You!HP Laptop WiFi Nightmare? Fix Your Windows 7 Connection NOW!
Alright, folks, gather 'round! Let's talk about something that's probably given us all a headache at some point: the dreaded WiFi connection issues on our HP laptops running the venerable Windows 7. Remember those days? The constant buffering, the dropped connections right in the middle of something important, the sheer frustration of staring at that little "No Internet Access" icon. Trust me, we've all been there. It's like trying to navigate a maze in a blizzard – disorienting, frustrating, and leaves you feeling like you're completely alone. But fear not! We're here to break down the mystery and get your HP laptop back online, and fast.
1. The Windows 7 WiFi Woes: A Blast From the Past… and a Headache?
Windows 7, a classic operating system that many of us still have on older HP laptops or have come across. It was a fantastic operating system, but it also had its quirks, especially when it came to WiFi. Imagine your laptop as a car: the WiFi adapter is the engine, the router is the gas station, and the internet is the open road. Now picture trying to drive that car with a sputtering engine or a faulty fuel line. That's what it often felt like when your Windows 7 HP laptop was battling WiFi issues.
2. Is Your Connection REALLY the Problem? The First Check.
Before we dive headfirst into troubleshooting, let's take a step back. Often, the problem isn't your laptop at all. Let's quickly check the basics:
- Is your router on? Sounds silly, right? But you wouldn't believe how often this is the issue! Check the power light.
- Is the internet working on other devices? Grab your phone, tablet, or another laptop. If those can connect, the problem is likely with your HP laptop. If they also can't connect, contact your internet provider.
- Are you within range of your WiFi signal? Walls, distance, and even certain appliances can weaken the signal. Try moving closer to your router.
3. The Dreaded "Limited Access" or "No Internet Access" Error: Decoding the Message.
This is the message that strikes fear into the hearts of Windows 7 users. It essentially means your laptop can "see" the WiFi network, but it can't get internet access. It's like your car recognizing the gas station but the pump refusing to work. What causes this? Let's explore common culprits:
- Incorrect Network Security Key: Is your WiFi password correctly entered? Double-check it! It's easy to mistype a character.
- IP Address Conflicts: When multiple devices on the same network share the same IP Address.
- Driver Issues: Your WiFi adapter might not have the correct drivers installed or has become corrupted.
- Firewall Interference: Your firewall might be blocking the connection.
4. Troubleshooting Steps: The WiFi Revival Kit
Time to roll up our sleeves and get to work! We'll start with some simple fixes and work our way up if needed. Think of this as our WiFi "revival kit":
- Restart Everything: We're not just talking about restarting your laptop, but also the router and modem. Turn everything off, wait 30 seconds, and turn them back on. Sometimes, a simple reset does wonders.
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter: Windows 7 actually has a built-in troubleshooter. Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray (the bottom-right corner of your screen) and select "Troubleshoot problems." Let Windows do its thing. It often finds and fixes common issues.
- Forget and Reconnect to the Network: Sometimes, a fresh start is all you need. Right-click the WiFi icon, select "Open Network and Sharing Center," click "Manage Wireless Networks," select your problematic network, and choose "Remove." Then, reconnect by entering your network key.
- Check Your IP Configuration: Open Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Start menu), type
ipconfig /all, and press Enter. Look for the "Default Gateway" – this is the IP address of your router. If the IP addresses are conflicting, then there is an error.
5. Driver Detective: Update or Reinstall Your WiFi Adapter Drivers.
Drivers are like the instruction manual for your hardware. If they're outdated or corrupted, things won't work correctly.
- How to Update Drivers:
- Open Device Manager (search for "Device Manager" in the Start menu).
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click your WiFi adapter (e.g., "Intel Wireless-N 7260") and select "Update driver software."
- Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." If Windows finds an update, let it proceed.
- How to Reinstall Drivers:
- Go to Device Manager and find your WiFi adapter under "Network adapters."
- Right-click and select "Uninstall."
- Restart your laptop. Windows will usually reinstall the driver automatically. If not, you might need to download the driver from the HP website for your specific laptop model.
6. Firewall Follies: Is Your Firewall a WiFi Villain?
Firewalls are designed to protect your computer, but sometimes they can be overzealous and block legitimate connections.
- Temporarily Disable Your Firewall: For testing purposes only, try temporarily disabling your Windows Firewall. Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Firewall. Click "Turn Windows Firewall on or off" in the left pane and select "Turn off Windows Firewall (not recommended)" for both "Private network settings" and "Public network settings." Remember to turn it back on afterward!
- Check Firewall Exceptions: If you don't want to disable the firewall entirely, you can create an exception for your WiFi adapter. In the Windows Firewall settings, click "Allow a program or feature through Windows Firewall" and make sure your network adapter has a green checkmark next to it.
7. The Static IP Address Solution: Manual Configuration Magic.
If your router isn't assigning an IP address correctly (or if you just want to be more in control), you can try setting a static (fixed) IP address for your laptop.
- Access Network and Sharing Center: Right click on the WiFi icon, the go to "Open Network and Sharing Center".
- Change Adapter Settings: In the left pane, click "Change adapter settings".
- Network Properties: Right click on your WiFi adapter, and go to "Properties".
- Select Protocol: Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)". Click "Properties."
- Use Static IP Address: Select the option stating "Use the following IP address."
- Set IP Settings:
- IP address: Use a free IP address.
- Subnet mask: Usually 255.255.255.0.
- Default gateway: This is usually the IP address of your router.
- DNS server: You can use your router's IP address, or public DNS servers like Google's (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4).
- **Save Changes and restart your computer
8. Channel Surfing: Finding the Optimal WiFi Channel.
WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. Sometimes, a channel is congested by other nearby networks which could interrupt the performance.
- Access Your Router's Settings: You'll need to know your router's IP address (look for it in the
ipconfig /alloutput in Command Prompt). Type the router's IP address into your web browser and enter the username and password (usually found on a sticker on the router itself). - Check the WiFi Channel: Look for settings related to "Wireless" or "WiFi." You should find an option to change the channel (usually a number from 1 to 11 or 1 to 13). Try different channels to see if it improves your connection.
9. The Power Saving Paradox: Disable Power Management for Your Adapter.
Sometimes, Windows 7's power-saving features can interfere with your WiFi connection.
- In Device Manager: Go to Device Manager (see step 5).
- Adapter Properties: Expand "Network adapters," right-click your WiFi adapter, and select "Properties."
- Power Management Tab: Go to the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the option: Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
10. Outdated Hardware? Considering a USB WiFi Adapter.
If all else fails, your WiFi adapter might be old, damaged, or simply incompatible with your router. A USB WiFi adapter offers an easy (and often affordable) solution. Plug it in, install the drivers, and you're back in business!
11. Resetting Network Settings: A Nuclear Option.
If you have exhausted all options, you can reset the network settings.
- Open Command Prompt: Open command prompt and run as administrator
- Use the command: Type
netsh winsock resetand press enter. - Restart:
Cara UpdateInstall Driver WIFI Secara Offline di PC atau Laptop

By WINTECH id Cara UpdateInstall Driver WIFI Secara Offline di PC atau Laptop by WINTECH id
Cara Download Dan Instal Driver Wifi Laptop & Komputer Bisa Untuk Windows 7,8,10,11

By logistech ID Cara Download Dan Instal Driver Wifi Laptop & Komputer Bisa Untuk Windows 7,8,10,11 by logistech ID
Cara mengatasi Wifi adapter hilang windows 7,8,10
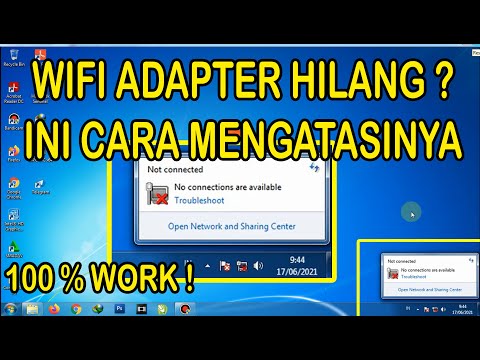
By Ani Saja Cara mengatasi Wifi adapter hilang windows 7,8,10 by Ani Saja

Title: CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7
Channel: Rdn Channel
CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7 by Rdn Channel
My Laptop Work
HP Laptop WiFi Nightmare? Fix Your Windows 7 Connection NOW!
Have you found yourself staring at the dreaded "no internet access" icon on your HP laptop, battling a frustrating WiFi connection? Are you running Windows 7 and tearing your hair out trying to get back online? You're not alone. Countless HP laptop users running Windows 7 experience intermittent or complete WiFi failures. But don't despair. This guide is your lifeline. We'll walk you through a systematic approach to diagnose and resolve the most common WiFi connection issues, restoring your precious internet access. Prepare to reclaim your online life.
Understanding the HP Laptop and Windows 7 WiFi Connection Challenge
HP laptops, renowned for their versatility, sometimes clash with the intricacies of Windows 7, especially concerning WiFi. The issue often stems from various factors, including driver incompatibilities, outdated software, network configuration glitches, and even hardware limitations. Recognizing the source of the problem is the first step to finding a comprehensive solution. Let’s dive into the crucial aspects of solving the WiFi conundrum.
Step 1: Verifying the Physical Connection and Wireless Adapter Status
Before we dive into complicated software configurations, let's begin with the basics. Is your WiFi adapter even enabled? This might seem elementary, but it’s a common oversight.
Checking the Physical WiFi Switch (if applicable): Many HP laptops have a physical switch, often located on the side or front of the chassis, that controls the WiFi adapter. Make certain that this switch is in the "on" position. It might have separate symbols, such as a radio tower or a WiFi icon.
Inspecting the Wireless Adapter in Windows 7:
- Click on the “Start” button and type "Device Manager" in the search bar. Press Enter.
- In the Device Manager window, locate “Network adapters.” Expand this category by clicking the arrow to the left.
- Here, you should see your wireless network adapter, typically identified by names such as "Intel Wireless," "Realtek Wireless," or similar.
- Look for any warning signs. Is there a yellow exclamation mark or red "X" superimposed on the adapter icon? These indicate problems, often driver-related.
If the adapter is disabled, right-click on it and select "Enable." If it's present and enabled, then continue to Step 2.
Step 2: Diagnosing the Windows 7 Network Connection
Windows 7 includes built-in troubleshooting tools that can provide insights into your WiFi issues. Utilize these tools as the next step in your assessment.
Running the Windows Network Troubleshooter:
- Click the network icon in the system tray (bottom right corner, near the clock). It looks like a set of bars or an Ethernet cable.
- If you see a red "X," that indicates a connection problem. Click on "Troubleshoot problems."
- Windows 7 will automatically diagnose and attempt to fix any issues it detects. Follow any on-screen prompts.
Checking IP Addresses and Network Settings:
- Open the "Network and Sharing Center." You can usually find it by right-clicking the network icon in the system tray and selecting “Open Network and Sharing Center.”
- Click on "Change adapter settings" (on the left side of the Network and Sharing Center).
- Right-click on your wireless network adapter and then click “Status.”
- In the “Status” window, click “Details.”
- Examine the details. Under "IPv4 Address," you should see an IP address. If it starts with 169.254.x.x, this suggests that your laptop isn't receiving a proper IP address from your router, indicating an issue.
If you see 169.254.x.x, proceed to the "Troubleshooting DHCP and Router settings" section.
Step 3: Addressing Driver Issues: The Key to Wireless Success
Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers are a frequent offender in WiFi woes. Ensuring your drivers are up-to-date is critical.
Updating the Wireless Network Adapter Driver:
- Open “Device Manager” (as described in Step 1).
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Update Driver Software…"
- Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows will attempt to find and install the newest driver.
If Windows cannot find an updated driver, or if the issue persists, you may need to perform a manual driver update.
Manually Updating the Driver:
- You will need to know the exact model of your network adapter (you can find this in Device Manager under "Network adapters").
- Visit the HP support website. Enter your laptop's model number or the serial number. This is the most reliable way to find drivers specific to your laptop.
- Navigate to the "Drivers" or "Software and Drivers" section for your model.
- Locate the drivers for your wireless adapter for Windows 7. Download the newest version.
- Run the downloaded driver installer. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the driver.
- Restart your laptop after installation.
Step 4: Troubleshooting DHCP and Router Settings
If you're receiving a 169.254.x.x IP address, the problem potentially lies in your Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) settings or your router's configuration.
Checking DHCP Configuration: DHCP is the mechanism by which your router assigns IP addresses to devices on your network.
- Restart Your Router: This often resolves minor DHCP hiccups. Unplug your router from the power outlet for about 30 seconds, then plug it back in. Wait for it to fully boot up.
- Check Router's DHCP Settings: Access your router's configuration page. Usually, you can access this through a web browser by typing your router's IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into the address bar; you will need the router’s username and password to login. Consult your router’s manual or the manufacturer's website for these credentials. Look for DHCP settings. Ensure DHCP is enabled. The DHCP range should include addresses your laptop can access.
- Consider a Static IP Address (Advanced): If DHCP still isn't working, try assigning a static IP address to your laptop. In the "Network and Sharing Center," click "Change adapter settings." Right-click on your wireless adapter and select "Properties." Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties." Under the "General" tab, select "Use the following IP address." Enter a valid IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server addresses. These must be configured in accordance with your network scheme.
Step 5: Reinstalling or Rolling Back Drivers for Stability
If recent driver updates seem to have caused issues, consider uninstalling the driver and reinstalling it with the correct drivers.
Uninstalling and Reinstalling the Current Network Adapter Driver:
- Open “Device Manager.”
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Uninstall."
- In the confirmation dialog, check the box to "Delete the driver software for this device" if available. Click "OK."
- Restart your laptop. Windows 7 should try to reinstall the driver automatically. If this does not work, then follow the steps mentioned in the "Manually Updating the Driver" section.
Rolling Back to a Previous Driver Version:
- Open “Device Manager.”
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click on your wireless network adapter and select "Properties."
- Go to the "Driver" tab.
- Click "Roll Back Driver" if the option is available. This will revert to the previously installed driver.
- Restart your laptop.
Step 6: Addressing Security and Network Authentication Issues
Incorrect security settings or issues with network authentication can also prevent WiFi access.
Verifying the Wireless Security Key:
- Reconnect to your WiFi network. When prompted for the security key, double-check that you are entering the correct password. Password errors may persist.
- If you are uncertain, check your router's configuration to view the current security key (often referred to as the "Password").
Checking Wireless Security Type:
- In "Network and Sharing Center," click "Manage wireless networks."
- Right-click on your WiFi network and select "Properties."
- In the "Security" tab, review the "Security type." Ensure it is set to a supported setting, such as WPA2-PSK or WPA-PSK. WEP is outdated and less secure, so avoid it.
Network Authentication Problems:
- If you frequently encounter authentication issues, try forgetting the network and re-entering the password. In "Manage wireless networks," right-click on the network and select "Remove network." Then, search for the network and re-enter the password.
- Sometimes the issue may be due to network congestion. Try connecting to the WiFi during non-peak hours to establish the connection.
Step 7: Advanced Troubleshooting: Running Diagnostics and Restoring Network Configuration
The following
