can t turn on wifi on laptop windows 10

Title: Turn WiFi Back On Manually Windows 10 Method 26
Channel: vHub
Turn WiFi Back On Manually Windows 10 Method 26 by vHub
can t turn on wifi on laptop windows 10, how to turn on wifi on laptop windows 10 pro, how to turn on wifi on laptop windows 10 lenovo, wifi won't turn on laptop windows 10, wifi won t turn on dell laptop windows 10, how to turn on wifi on dell laptop windows 10, how to turn on wifi on hp laptop windows 10, how to turn on wifi on acer laptop windows 10, how to turn on wifi on asus laptop windows 10, how to turn on wifi on toshiba laptop windows 10
WiFi Nightmare on Windows 10? FIX IT NOW!
Wi-Fi Woes on Windows 10? Conquer the Connection Chaos!
Are you wrestling with a Windows 10 Wi-Fi that's more temperamental than a toddler at bedtime? Do dropped connections, sluggish speeds, and the dreaded "limited connectivity" message haunt your digital life? You're not alone. This frustrating reality plagues countless users. But fret not! There's a light at the end of the tunnel – or, at least, a stable Wi-Fi signal waiting to be rediscovered. Let's dive into some potent solutions.
Is Your Router the Culprit? First Steps to Wireless Sanity.
Before you blame your operating system entirely, let's consider the obvious. Sometimes, the source of the problem lies elsewhere. Moreover, a quick check of your router's status is a good starting point. So, is your router powered on, and are its indicator lights behaving predictably?
First, reboot the router. This simple fix resolves a surprising number of Wi-Fi glitches. To do this, unplug it from the power source, wait a minute, and plug it back in. After the reboot, try connecting again.
On the contrary, if the problem persists, inspect your router's physical location. Walls, especially those made of concrete or brick, can significantly impede Wi-Fi signals. Metal objects also act as signal blockers. Furthermore, relocate your router to a more open area. You might experience a dramatic improvement.
Windows 10 Wi-Fi Troubleshooter: Your Digital Detective.
Fortunately, Windows 10 offers a built-in troubleshooter. It's a surprisingly effective tool. It can often pinpoint and resolve common Wi-Fi problems automatically.
To access it, navigate to your "Settings" menu. Click on "Network & Internet," then "Status." Scroll down and select "Network troubleshooter." Follow the on-screen prompts, and let Windows perform its diagnostic magic. Sometimes, this alone can bring your Wi-Fi back to life. Conversely, ensure you're running the latest version of Windows 10. System updates often include Wi-Fi driver improvements.
Driver Dilemmas: Update, Roll Back, or Reinstall.
Outdated or corrupted network drivers are a common cause of Wi-Fi woes. Therefore, updating your network adapter's driver is a crucial step.
To update your driver, open the Device Manager, which you can find by searching for it in the Windows search bar. Expand the "Network adapters" section. Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter (e.g., "Intel Wireless-AC 9260"), and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will search online and install the latest drivers if available.
However, if the update causes more problems, a driver rollback may be necessary. In the Device Manager, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter again and select "Properties." Go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver" if the option is available. If it's not, you can also consider uninstalling your network adapter driver. Reinstalling it may resolve the connection issues.
Network Settings: Fine-Tuning Your Connection.
Sometimes, the problem lies within your network settings. Now we will look at a few things you can try.
Firstly, make sure your network adapter is enabled. In the Device Manager, ensure your Wi-Fi adapter isn't disabled. If it is, right-click and select "Enable device."
Secondly, check your network settings. If you are using a static IP address, ensure it is correctly configured. Incorrect settings can cause connectivity problems. Furthermore, you can revert to automatically obtaining IP addresses.
Another thing to consider is resetting your network settings. In Settings, head to "Network & Internet" then "Status." Click "Network reset" to reset these settings to their defaults. Keep in mind, this will also reset your network adapters.
Channel Conflicts and Interference: Optimizing Your Wireless Environment.
Wi-Fi signals operate on specific channels. Neighboring networks can sometimes cause interference if they're using the same channel. This interference can lead to dropped connections and slow speeds.
To resolve this, log into your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser) and change the Wi-Fi channel. Different routers have different steps to do this, so consult your router's manual. Try different channels to find the one that provides the best performance. Furthermore, ensure your router isn't near devices that cause interference, such as microwaves or cordless phones.
Advanced Fixes: Diving Deeper into the Digital Depths.
If the above solutions haven't worked, let's venture into more advanced territories.
Firstly, consider disabling your firewall, especially if you are using a third-party firewall. Sometimes, firewalls block wireless connections. It is important to note that, while troubleshooting, you should disable your firewall temporarily. Ensure you re-enable it afterward for security reasons.
Secondly, check your DNS settings. You can change the DNS server addresses your computer uses. Using public DNS servers like Google's (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) can improve speed and reliability.
Finally, sometimes, a clean boot can help. A clean boot starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and startup programs. This can help identify if a conflicting application is causing the Wi-Fi issues.
Victory! Conquering Connectivity Challenges.
Dealing with Wi-Fi problems can be incredibly frustrating. But with patience and these solutions, you can often restore your wireless connection. Moreover, by systematically working through these steps, you're well-equipped to conquer those Windows 10 Wi-Fi nightmares. With your Wi-Fi working flawlessly, you can resume your digital life!
**Turn Your Laptop into a WiFi Hotspot in 60 Seconds! (Windows 10)**WiFi Nightmare on Windows 10? FIX IT NOW!
Alright, let's be honest, we've all been there. You're in the middle of something important – maybe a crucial video call, a nail-biting online game, or simply trying to stream your favorite show – and BAM! The dreaded WiFi drops out. Windows 10 has its quirks, and a flaky WiFi connection is often at the top of the list. But don't despair, because we're going to dive headfirst into the WiFi trenches and wrangle that stubborn connection back into submission. Think of this guide as your personal WiFi rescue mission. We’ll explore the common culprits, troubleshoot like seasoned IT veterans, and get you back online pronto. Ready to say goodbye to the buffering blues? Let's roll!
1. The Phantom Disconnect: Why Is My WiFi Being So Rude?
First things first, let's identify the enemy. Why is your Windows 10 WiFi constantly giving you the cold shoulder? The reasons are as varied as snowflakes, but here are some of the usual suspects:
- Driver Corruption: Think of drivers as the translators between your hardware (your WiFi adapter) and your operating system (Windows 10). If these translators are garbled, things get lost in translation, leading to disconnects.
- Router Issues: Your router is the gatekeeper to the internet. If it's overloaded, outdated, or just plain cranky, it can cause WiFi woes. It's like the grumpy bouncer at a club; everyone wants in, but only some get through.
- Windows Updates Gone Wrong: Sometimes, those helpful Windows updates, designed to improve your experience, can actually break things. They might introduce new bugs or conflict with existing drivers.
- Interference: Think of your WiFi signal as a radio station. Other devices emitting radio waves (microwaves, Bluetooth devices, even your neighbor's WiFi) can interfere with your signal, causing dropouts.
- Power Management Settings: Windows 10, in its quest to save battery life (especially on laptops), might be throttling your WiFi adapter, causing it to power down when it shouldn't. It’s like trying to run a marathon with your legs tied together.
2. Driver Delinquents: Updating Your WiFi Adapter
This is often the first port of call. Outdated or corrupted drivers are a common cause of WiFi problems. Here's how to get things shipshape:
Open Device Manager: Right-click the Start button and select "Device Manager." It's your control panel for your hardware. (Think of it as your internal mechanic's garage).
Find Your Network Adapter: Expand the "Network adapters" section. You'll see your WiFi adapter listed there (it might be called something like "Wireless Network Adapter" or "Wi-Fi").
Update the Driver: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." You'll be given two options:
- Search automatically for drivers: Windows will try to find the latest drivers online. Cross your fingers and hope for the best!
- Browse my computer for drivers: Choose this if you've already downloaded the driver from the manufacturer's website (more on this later).
Restart Your Computer: Once the driver update is complete, restart your PC. Like a fresh reboot after a bad day, it can often clear up lingering issues.
Pro Tip: If the automatic update fails, head to your computer manufacturer's website (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) or the website of your WiFi adapter manufacturer (e.g., Intel, Broadcom) and download the latest drivers specifically for your Windows 10 version. This is like getting a custom tune-up.
3. Router Reboot: The Simplest WiFi Cure?
Before you get too deep into the tech weeds, let's try the simplest solution – the router reboot. Often, this is all it takes to clear up a sluggish or intermittent connection.
Unplug Your Router: Unplug your router from the power outlet. This is like giving it a digital detox.
Wait a Bit: Give it a good 30 seconds to a minute – like a mini-vacation for your router.
Plug It Back In: Plug the router back in and wait for it to fully boot up. This can take a few minutes.
Test Your Connection: See if the WiFi is working. Fingers crossed!
4. Troubleshooting the Router: Digging Deeper
If a simple reboot doesn't do the trick, it's time to investigate your router.
- Check the Lights: Are all the lights on your router glowing the way they should? Look for a solid Internet connection indicator. If something's blinking red (or not at all), that's a clue.
- Check Your Internet Speed: Run a speed test (e.g., using speedtest.net) to see if you're getting the speeds you're paying for. Slow speeds might indicate a problem with your internet service provider (ISP).
- Router Firmware: Is your router firmware up-to-date? Just like your computer, your router has software that needs occasional updates. Check your router's manual for instructions on how to update the firmware. This is like upgrading the brain of your router.
- Router Placement: Is your router hidden in a cupboard or crammed behind other devices? It needs a clear line of sight to transmit its signal effectively. Try moving it to a more central, open location.
5. Windows Update Blues: Reverting to a Previous Version
Sometimes, a recent Windows update can be the culprit. If you suspect this is the case, you can revert to a previous version of Windows.
Go to Settings: Click the Start button and then click the gear-shaped "Settings" icon.
Update & Security: Click on "Update & Security."
Recovery: In the left-hand menu, click "Recovery."
Go Back to a Previous Version: If Windows allows it (usually within 10 days of the update), you'll see an option to "Go back to the previous version of Windows 10." Proceed with caution, as this can revert changes and updates, so back up any essential files before you start.
6. Power Management Mayhem: Taming Your Adapter
As mentioned earlier, Windows 10 might be putting your WiFi adapter to sleep to save power. Let's tell it to behave!
Open Device Manager (Again): Right-click the Start button and select "Device Manager."
Network Adapters: Expand "Network adapters."
Properties: Right-click your WiFi adapter and select "Properties."
Power Management Tab: Click the "Power Management" tab.
Uncheck the Box: Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This is like giving your WiFi adapter a permission slip to stay awake. Click "OK".
7. Channel Surfing: Minimizing Interference
Your WiFi router broadcasts on a specific channel. Other routers in your area can interfere with your signal, making your connection unstable. The solution? Switch to a less crowded channel.
Access Your Router's Settings: You'll need to log in to your router's control panel. This is usually done by typing your router's IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into your web browser. You'll need your router's username and password, which can usually be found on a sticker on the router itself or in its documentation.
Wireless Settings: Locate the "Wireless" or "Wi-Fi" settings in your router's control panel.
Channel Selection: Look for the "Channel" or "Wireless Channel" setting. The default is often "Auto," which may be the issue.
Choose a Channel: Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are generally recommended as they are less prone to interference ). You might need to try a few different channels to find the best one. Save your settings and reboot your router.
8. Network Reset: The Nuclear Option (But It Works!)
If everything else fails, Windows 10 has a network reset feature that can restore all your network settings to their default values. This is like a digital reset button. Be aware that you'll need to re-enter your WiFi password afterward.
Go to Settings: Click the Start button and then click the gear-shaped "Settings" icon.
Network & Internet: Click on "Network & Internet."
Network Reset: Scroll down and click "Network reset."
Reset Now: Follow the prompts to reset your network settings. Your computer will restart.
9. Reinstall Network Adapter: Fresh Start
Sometimes, a complete reinstall of the network adapter can do the trick.
Open Device Manager: Right-click the Start button and select "Device Manager."
Network Adapters: Expand "Network adapters."
Uninstall: Right-click your WiFi adapter and select "Uninstall device."
How to Turn on Wifi on Window 10 in Laptop Wifi Not Turning on Problem Solved Wifi Turned Off
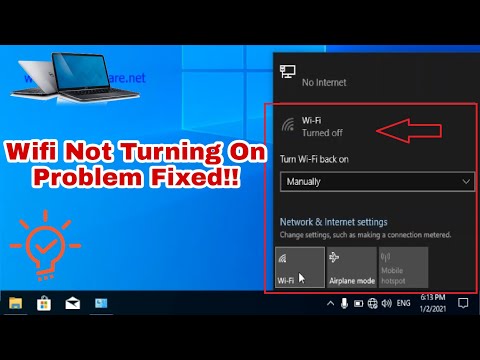
By Zeeshan Awan How to Turn on Wifi on Window 10 in Laptop Wifi Not Turning on Problem Solved Wifi Turned Off by Zeeshan Awan
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
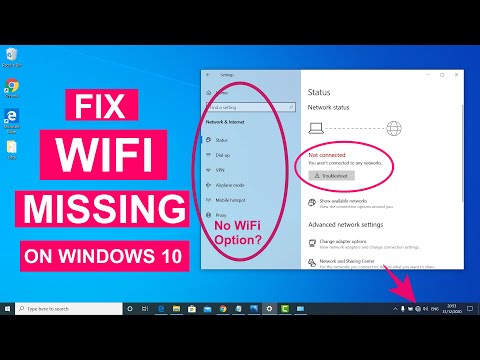
By Sandeep Singh Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit

By Howtosolveit How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit

Title: how to turn on wifi on Windows 10 in laptop l wifi not Turning on problem solved l wifi turned off
Channel: Rasik Khoradiya
how to turn on wifi on Windows 10 in laptop l wifi not Turning on problem solved l wifi turned off by Rasik Khoradiya
Working With Laptop
WiFi Nightmare on Windows 10? FIX IT NOW!
Have you recently found yourself wrestling with a frustratingly unreliable WiFi connection on your Windows 10 device? Constant dropouts, sluggish download speeds, and a general feeling of digital sluggishness can quickly transform your online experience into a series of irritating setbacks. Rest assured, you are not alone. Countless Windows 10 users encounter these same WiFi woes, and, thankfully, the solutions are often simpler than you might imagine. We’re here to guide you through a comprehensive troubleshooting process, designed to banish those WiFi nightmares and restore the seamless connectivity you deserve. Let's dive in and get your internet flowing smoothly again!
Understanding the Source of Your WiFi Headaches
Before we begin implementing fixes, it's helpful to understand the common culprits behind WiFi problems in Windows 10. While the specific cause can vary, several factors often contribute to these connectivity struggles:
- Driver Issues: Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible network adapter drivers are frequently the root of the problem. These drivers act as the communication bridge between your computer and your WiFi hardware, and any glitch can lead to connection failures.
- Network Adapter Configuration: Incorrect settings within your network adapter’s properties can inadvertently restrict or hinder your connection. Power-saving settings, for instance, can be overzealous, leading to intermittent disconnections.
- Router Conflicts: Your router, the central hub of your home network, might be causing issues. Firmware updates, channel congestion, or hardware limitations can all contribute to a subpar WiFi experience.
- Windows 10 Updates: While generally beneficial, Windows 10 updates can sometimes introduce unforeseen compatibility issues with network adapters or drivers.
- Interference: External factors, such as other electronic devices (microwaves, cordless phones) or physical obstacles (walls, distance), can interfere with your WiFi signal.
Step 1: The Simple Solutions - Quick Fixes to Try First
Before diving into more complex troubleshooting, always explore these straightforward solutions. They often resolve the most common WiFi issues:
- Restart Your Computer and Router: This classic troubleshooting tactic frequently works wonders. Restarting clears temporary glitches and re-establishes connections. Unplug your router and modem for about 30 seconds before plugging them back in. Allow them to fully boot up before your computer.
- Check the WiFi Switch: Make sure the WiFi switch on your laptop (if applicable) is turned on. This might seem obvious, but it's a common oversight.
- Airplane Mode: Toggle Airplane mode on and then off. This resets your network adapters and can sometimes jumpstart a stalled connection.
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter: Windows includes a built-in troubleshooter designed to detect and fix common network problems. Access it by searching for "Network troubleshooter" in the Windows search bar. Follow the prompts and see if it identifies and resolves any issues.
Step 2: Driver Management - Ensuring Your Network Adapter Is Up-to-Date
Network adapter drivers play a pivotal role in your internet connectivity. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause a host of WiFi problems. Let's ensure your drivers are in top shape:
- Accessing Device Manager: Right-click the Start button and select "Device Manager." Alternatively, type "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar and select it from the results.
- Locating Your Network Adapter: In Device Manager, expand "Network adapters." You will see a list of your network adapters, including your WiFi adapter (often labeled with "Wireless" or "WiFi").
- Updating Drivers: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will then attempt to locate and install the latest drivers. If Windows finds and installs a new driver, restart your computer.
- Manual Driver Updates: If the automatic update fails, try manually updating the driver. Visit the website of your computer manufacturer (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) or the manufacturer of your network adapter (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, Realtek). Download the latest driver for your specific model and operating system. Install it by right-clicking your WiFi adapter in Device Manager, selecting "Update driver," and then choosing "Browse my computer for drivers." Navigate to the location where you saved the downloaded driver and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Rolling Back Drivers: If a recent driver update caused the WiFi issues, you can roll back to a previous driver version. In Device Manager, right-click your WiFi adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver." If the option is grayed out, it means there is no previous driver to revert to.
- Uninstalling and Reinstalling: In Device Manager, you can uninstall the driver and then restart your computer. Upon restarting, Windows will often reinstall the driver automatically. This can often resolve driver-related conflicts. Right-click your WiFi adapter, select "Uninstall device," and confirm the removal.
Step 3: Network Adapter Settings - Tweaking for Optimal Performance
Once you've addressed the drivers, consider adjusting the settings of your network adapter. These adjustments can often improve stability and performance:
- Accessing Adapter Properties: In Device Manager, right-click your WiFi adapter and select "Properties."
- Advanced Tab: Go to the "Advanced" tab. This tab displays a list of configurable properties. The specific options and their names will vary depending on your adapter.
- Power Saving: Find any power-saving related options (e.g., "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power"). Disable them. Power-saving features can sometimes interfere with the WiFi connection.
- 802.11n/ac Mode: Look for settings related to the 802.11n or 802.11ac standards (the latest WiFi standards). Make sure these are not disabled. These represent the speeds and capabilities of your WiFi connection. If you are using a router that supports newer wifi standards, you should make sure these options are enabled to use these faster speeds on your wireless connection.
- Wireless Mode Selection: Change the setting that states the mode of connection to your access point. For example, if your network's access point provides both b/g/n modes, you'll see an option on your network adapter properties. Choose the most compatible mode that your access point offers. If unsure, choose the highest mode available on your router.
- MTU Size: Sometimes, adjusting the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) size can help. You can try different MTU values, starting with 1472, and testing your connection. If unsure, set it to "Auto."
- Restart After Changes: After making any changes to your network adapter properties, restart your computer for them to take effect.
Step 4: Router Configuration - Fine-Tuning Your Network's Heartbeat
Your router is the central point of your network, and its settings can significantly impact your WiFi experience:
- Router Firmware Updates: Ensure your router's firmware is up-to-date. Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and fix bugs. Access your router's web interface (usually by typing its IP address into a web browser – often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 – and entering your router's username and password). Look for a "Firmware" or "Update" section.
- WiFi Channel Selection: WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. Congestion on a specific channel can lead to slower speeds and intermittent connections. The channel may be set to "auto" to let the router choose the best one, or you can manually change it. Access your router's web interface and go to the WiFi settings. Look for a channel selection option. Experiment with different channels (e.g., 1, 6, or 11 for 2.4 GHz networks, or different channels for 5GHz networks) to see if it improves performance.
- Router Placement: The physical location of your router is important. Position the router in a central location in your home, away from walls, metal objects, and other potential sources of interference. Elevating the router can also help improve signal coverage.
- Router Reboot and Factory Reset: Perform a full factory reset. Be aware that this will wipe out all of your custom router settings, so you'll need to reconfigure your WiFi network. Find the reset button on the router (often a small recessed button) and hold it down for about 15-30 seconds while the device is powered on. After resetting your router, you will need to access the web interface and set up your WiFI configuration.
- 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz: Modern routers often broadcast on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band offers longer range but can be slower and more prone to interference. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and less interference but has a shorter range. Make sure you are connecting to the appropriate band for your needs and the capabilities of your devices. Consider using the 5GHz band if your device and router support it, and you are close enough to the router.
Step 5: Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques - Digging Deeper
If the above steps haven't resolved the WiFi issues, consider these more advanced techniques:
- Network Reset: Windows 10 offers a network reset feature that
