wifi not showing up on laptop windows 10

Title: How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit
Channel: Howtosolveit
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit
wifi not showing up on laptop windows 10, wifi network not showing up on laptop windows 10
WiFi Vanished?! Fix Your Windows 10 Connection NOW!
My Wi-Fi's Gone AWOL! A Windows 10 SOS Guide
Have you experienced the sudden disappearance of your Wi-Fi? Don’t panic! This frustrating scenario happens more often than you think. It’s a digital disappearing act that can leave you stranded. I'll help you get back online. Let's delve into some immediate troubleshooting steps. We'll get your Windows 10 connection resurrected.
Is Your Digital Life on Hold? Check the Obvious First.
Before diving into the techy stuff, perform a simple reality check. Firstly, confirm your modem and router are powered on. Secondly, check the lights. Do they indicate a stable internet connection? Sometimes, a simple power cycle is all it takes. Unplug both devices. Wait for a minute. Then, plug them back in. Let them reboot fully. Consequently, test your connection again.
Furthermore, are other devices connected? If your phone and tablet are also offline, the issue is probably with your internet provider. Thus, contact them to report an outage. However, if other devices have Wi-Fi, the problem may be with your Windows 10 PC.
Windows 10 Wi-Fi Woes: The Troubleshooter to the Rescue!
Windows 10 offers a built-in troubleshooter. It is a handy tool. The troubleshooter identifies and fixes common network problems. Access it by searching "Network troubleshooter" in the Windows search bar. Run it. Let it do its work. Afterwards, it will suggest solutions. Sometimes, this solves the problem instantly.
The troubleshooter can identify common culprits. These include incorrect network settings. For instance, it can also fix driver issues. Therefore, don’t underestimate its power. It's often the first step to take.
Driver Dilemmas: Could It Be Your Wireless Adapter?
Your wireless adapter is the heart of your Wi-Fi connection. So, outdated or corrupted drivers can cause issues. You can check your wireless adapter driver. Go to Device Manager. You can access the Device Manager by right-clicking the Start button. Then, select "Device Manager" from the menu.
Expand "Network Adapters." Look for your wireless network adapter. Right-click it. Select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Alternatively, browse to your manufacturer's website. Download the latest drivers. Therefore, make sure you install them correctly. Restart your computer after any driver updates.
Network Connections: Are You Even Connected?
Windows 10 might be inadvertently disconnected from your network. Thus, you must verify your connection. Click the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray. Consequently, ensure the correct Wi-Fi network is selected. Make sure it says "Connected".
If not, select your network. Enter your password if prompted. Furthermore, double-check that you're not in airplane mode. It cuts off all wireless connections. Consequently, turn it off. Look for the airplane symbol in the system tray.
The Nuclear Option: Resetting Your Network Settings
If all else fails, it's time to consider a network reset. Bear in mind that this will reset all network settings. You'll need your Wi-Fi password again. Consequently, it often resolves persistent connection problems.
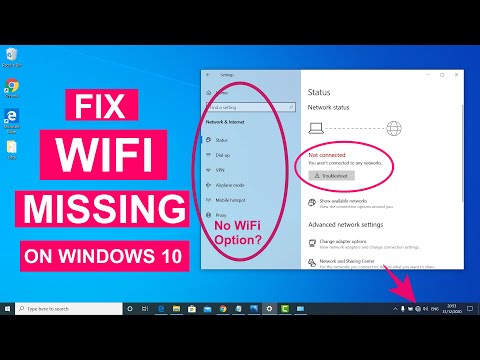
Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status. Scroll down. You'll find the "Network reset" option. Click it. Then, confirm your decision to reset. Windows will restart. Expect a slight delay. Try connecting to your Wi-Fi again. Enter your password.
Antivirus Interference: A Silent Culprit
Sometimes, your antivirus software blocks the Wi-Fi connection. Therefore, temporarily disable your antivirus. Then, test your connection. If the Wi-Fi works, your antivirus is the problem. Reconfigure its settings. Allow the Wi-Fi connection. Otherwise, contact your antivirus provider for support.
IP Address Conflicts: A Network Clash
IP address conflicts can cause connectivity issues. This happens when two devices have the same IP address on the network. In this scenario, your router could be the root cause. You can try renewing your IP address. Open Command Prompt as an administrator. Type "ipconfig /release". Hit Enter. Then, type "ipconfig /renew". Hit Enter again. After that, restart your computer.
Last Resort: System Restore
Consider System Restore. This brings your computer back to an earlier state. It reverts to a time when your Wi-Fi worked. Search for “Create a restore point”. Create a new one if you haven't already. Then, choose a restore point before the Wi-Fi started acting up. Ultimately, this can rectify software-related problems.
Staying Connected: Proactive Measures
Prevent future Wi-Fi woes. Perform regular driver updates. Protect your network with a strong password. Also, consider a router upgrade. Keep your Windows 10 updated. Following these tips can minimize issues. Ultimately, you'll enjoy uninterrupted connectivity. Hopefully, this guide has helped you get back online. Go forth and browse!
iPhone & Laptop Backup: Wireless Freedom (No Wires!)WiFi Vanished?! Fix Your Windows 10 Connection NOW!
Ever been there? You're in the middle of something crucial – maybe a video call for work, streaming your favorite show, or even just trying to update your social media – and bam! Your Wi-Fi connection decides to take a vacation. The dreaded "no internet access" message stares back at you, taunting your productivity and your sanity. We've all been there. And honestly, it's infuriating. But don't panic! Before you hurl your laptop out the window (we understand the impulse!), let’s dive into how to troubleshoot and get your Windows 10 Wi-Fi back in action. We're going to be your digital Sherpas, guiding you up the mountain of connectivity woes.
1. The Initial Hiccup: Checking the Obvious First
Before we delve into the technical nitty-gritty, let's start with some common-sense checks. It's like making sure the car has gas before tearing apart the engine.
- Is your router on and plugged in? Seriously, it sounds silly, but it's happened to the best of us! Check the power light on your router and modem. If it's not lit, you've found your first suspect. Unplug it, wait 30 seconds, and plug it back in. Let it reboot. Sometimes, all it needs is a fresh start.
- Are other devices connected? Grab your phone, tablet, or another laptop. If they can't connect either, the problem is likely with your internet service provider (ISP) or your router, rather than your specific Windows 10 machine. Give them a call. They've got the support to identify and fix it.
- Did you accidentally hit the Wi-Fi off switch? Look for a physical Wi-Fi switch on your laptop. Some laptops have a dedicated button or a key combination (often Fn + a function key) that toggles Wi-Fi on and off. Ensure it's set to "on." It's like searching the house before you lose your keys.
2. The Windows 10 Troubleshooter: Your First Line of Defense
Windows 10 has a built-in troubleshooter designed to diagnose and fix common network problems. It's like having a tech-savvy friend on speed dial.
Go to:
- Settings (the gear icon in the Start menu or search for it)
- Network & Internet
- Status
- Click on “Troubleshoot problems”
- Follow the on-screen instructions. The troubleshooter will go through a series of checks and suggest solutions. It might reset your network adapter, which often resolves minor connectivity issues. Give it a shot!
3. Checking Your Network Adapter Driver: The Unsung Hero
Your network adapter driver is the software that allows your computer to "speak" to your Wi-Fi card. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause serious connection problems. Think of it as the interpreter between your computer and the internet.
Here's how to check and update it:
- Press the Windows key + X and select Device Manager.
- Expand "Network adapters." You'll see a list of your network adapters (e.g., Intel Wireless-AC 9560).
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Update driver."
- Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Let Windows find and install the latest version. If that doesn’t work.
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter again and select "Update driver."
- Choose "Browse my computer for drivers," then "Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer."
- Select the driver most recently installed, and click Next.
If the update doesn't work or shows an error, you might need to uninstall and reinstall the driver. In Device Manager, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Uninstall device," and restart your computer. Windows should automatically reinstall the driver on the next boot. Or, go to your laptop manufacturer's website to grab the latest driver to install.
4. Airplane Mode: A Quick Reset?
Airplane mode can sometimes work wonders. Activating it and deactivating it often forces your Wi-Fi adapter to reset.
- Click the network icon in your system tray (bottom right corner).
- Turn on Airplane mode. Wait a few seconds.
- Turn off Airplane mode. See if your Wi-Fi connection returns. It’s like a computer’s on-off button.
5. Forget and Reconnect to Your Wi-Fi Network: Fresh Start
Sometimes, your computer’s connection to your Wi-Fi network has become corrupted. Forgetting the network and reconnecting can be a simple fix.
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray.
- Click "Network & Internet settings"
- Click "Manage Wi-Fi settings."
- Look for the name of your Wi-Fi network in the list of "Manage known networks."
- Click on your network name and then select "Forget."
- Click on the Wi-Fi icon again and select your network.
- Enter your Wi-Fi password when prompted.
6. IP Address Issues: Static vs. Dynamic
Your computer needs an IP address to communicate on the network. Sometimes, the IP address configuration can cause problems. Let's verify it.
- Press the Windows key + R, type "ncpa.cpl," and press Enter. This opens the Network Connections window.
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Properties."
- Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties."
- Ensure that "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected.
- Click OK and then close the window. Restart your computer.
- If they are already set to "automatic," you can try setting them up manually. Not the best choice for the average user, but if you want to set static IP address, consult with your network administrator, or contact your ISP.
7. Flush the DNS Cache: Clean Slate
Your computer stores a cache of DNS (Domain Name System) information. Sometimes, this cache can become corrupted and cause issues. Flushing the DNS cache is like cleaning out the cobwebs.
- Press the Windows key + X, type "cmd," and click "Run as administrator."
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
ipconfig /flushdnsipconfig /registerdnsipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew
- Restart your computer.
8. Checking Your Antivirus/Firewall: Gatekeepers
Your antivirus software or firewall might be blocking your Wi-Fi connection. Often, it's a misconfiguration, but it's worth investigating.
- Temporarily disable your antivirus software (remember to turn it back on later!). See if your Wi-Fi connection returns.
- Check your firewall settings. Make sure your Wi-Fi adapter is allowed to communicate over the network. Consult your antivirus software's documentation for how to do this.
9. Router Interference: The Hidden Culprit
Other devices can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Think of it like shouting over a crowded room.
- Move your router away from other electronic devices (microwaves, cordless phones, other Wi-Fi routers).
- Consider the router's placement. Elevate it and center it somewhere, not in a corner.
- Change your Wi-Fi channel. Most routers automatically select a channel, but you can manually choose a less congested one in your router's settings. Consult your router's manual for instructions.
10. Reset Network Settings: Last Resort
If nothing else works, resetting your network settings is like starting from scratch.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset
- Click "Reset now." This will restart your computer. You'll need to re-enter your Wi-Fi password.
11. Physical Damage: The Hardware Issue
Sometimes, it's a hardware problem. Unfortunately, if none of these steps resolve the issue, the Wi-Fi adapter in your laptop might be damaged.
- Check Device Manager again for any errors related to your network adapter.
- Consider a USB Wi-Fi adapter. They are relatively inexpensive and can provide a temporary or permanent solution.
- Consult a computer repair professional, who can diagnose and potentially replace the Wi-Fi adapter.
12. Power Saving Mode: A Hidden Thief
Windows often has power-saving settings enabled for your network adapter. This can starve the Wi-Fi and prevent it from functioning properly.
- Go to Device Manager (as we discussed above).
- Expand Network Adapters, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and select "Properties."
- Click the "Power Management"
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
By Sandeep Singh Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
All But My WiFi Network Not Appeared Solved 2020

By Simplify All But My WiFi Network Not Appeared Solved 2020 by Simplify
Fix No WIFI networks found in Windows 10 11 How To Solve not showing available wi-fi Networks

By Victor Explains Fix No WIFI networks found in Windows 10 11 How To Solve not showing available wi-fi Networks by Victor Explains

Title: Fix 5ghz Wi-Fi Not Showing Up in Windows 11 10 How To Switch From 2.4Ghz to 5Ghz wifi
Channel: Victor Explains
Fix 5ghz Wi-Fi Not Showing Up in Windows 11 10 How To Switch From 2.4Ghz to 5Ghz wifi by Victor Explains
Wifi On Laptop Phone
WiFi Vanished?! Fix Your Windows 10 Connection NOW!
The wireless world, once a shimmering promise of seamless connectivity, can abruptly transform into a frustrating realm of dropped signals and maddening disconnections. You're in the middle of an important video call, streaming your favorite show, or perhaps even working on a critical project, and suddenly, poof—the WiFi signal evaporates. Fear not, because we're here to guide you through the troubleshooting process and get your Windows 10 device back online. We'll navigate the digital labyrinth and restore your access to the internet, swiftly and efficiently.
Identifying the Culprit: Pinpointing the Source of Your WiFi Woes
Before we dive into solutions, let's take a moment to consider the potential causes of your vanished WiFi connection. Is it a local issue, affecting only your device, or is the problem more widespread? A systematic approach to diagnosis is key.
Check the Obvious: Start with the fundamentals. Is your router plugged in and powered on? Are the indicator lights displaying a healthy signal (usually a solid blue or green)? A simple reboot of your router and modem can often resolve temporary glitches. Unplug both devices, wait a full minute, and then plug the modem back in first, followed by the router. Allow sufficient time for them to re-establish their connections.
Device-Specific or Network-Wide? Attempt to connect other devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops) to your WiFi network. If those devices also struggle to connect or experience intermittent disconnections, the issue likely resides with your router or internet service provider (ISP). If other devices connect without a problem, the problem is specific to your Windows 10 device.
Windows 10 Updates: A Blessing and a Curse: Windows 10 updates, while designed to enhance your system, can sometimes introduce conflicts, especially concerning network drivers. The latest update could inadvertently disable or corrupt your wireless adapter. We'll explore how to address this in more detail later.
Troubleshooting Your Windows 10 Wireless Adapter: A Deep Dive
Assuming the problem stems from your Windows 10 device, consider these targeted solutions:
The Airplane Mode Check: The Airplane Mode setting, located in the Action Center or via the system tray icon, can inadvertently disable your wireless adapter. Ensure that Airplane Mode is off. If it's on, your WiFi connection will be disabled.
Wireless Adapter Enable/Disable: Sometimes, a simple toggle will fix the issue. Navigate to the Network Connections settings panel. Right-click the WiFi adapter and select "Disable." Wait a few seconds, then right-click again and select "Enable." This often resets the adapter and re-establishes the connection. To access Network Connections, right-click the Start button and select "Network Connections," or use the search bar to find "Network Connections."
Driver Updates: The Crucial Step: Outdated or corrupted network drivers are a common culprit. Here's how to update or reinstall them:
- Open Device Manager: Search for "Device Manager" in the search bar.
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Locate your wireless adapter (it may be labeled with the manufacturer's name, such as Intel, Realtek, or Broadcom).
- Right-click the adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers" to let Windows find and install the latest version. Or, choose "Browse my computer for drivers" and manually direct Windows to scan your computer for drivers. If there is a driver installed prior, you can choose to uninstall and reinstall the driver.
- If automatic updates fail, you may need to visit the manufacturer's website (Intel, etc.) and download the latest drivers for your specific adapter and Windows 10 version.
- After updating the driver, restart your computer.
Driver Rollback: A Reversal of Fortune: If the problem arose after a recent driver update, you may consider rolling back to a previous driver version:
- Open Device Manager.
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click your wireless adapter.
- Select "Properties."
- Go to the "Driver" tab.
- If the "Roll Back Driver" button is active, click it. This reverts to the previously installed driver.
- Restart your computer.
Network Troubleshooting: Windows 10's Built-In Tools
Windows 10 provides built-in troubleshooting tools that can automate the diagnostic process and often resolve connectivity issues:
The Network Troubleshooter:
- Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray (or the network icon if you're using Ethernet).
- Select "Troubleshoot problems."
- Follow the on-screen instructions. The troubleshooter will attempt to identify and fix common network problems.
Network Reset: This feature resets all network adapters to their default settings, potentially resolving underlying conflicts. Beware: This will erase any custom network settings you have.
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status.
- Click on "Network reset" at the bottom of the page.
- Click "Reset now" and confirm the action.
- Your computer will restart. After the restart, you'll need to reconnect to your WiFi network by entering your password.
Advanced Solutions: Delving Deeper
If the previous steps haven't resolved the issue, consider some more advanced techniques:
Flush DNS Cache: The Domain Name System (DNS) cache stores website addresses for faster browsing. Sometimes, corrupted entries in the DNS cache can interfere with your internet connection. To flush the DNS cache:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator (search for "cmd," right-click "Command Prompt," and select "Run as administrator").
- Type
ipconfig /flushdnsand press Enter. - Type
ipconfig /registerdnsand press Enter. - Type
ipconfig /releaseand press Enter. - Type
ipconfig /renewand press Enter. - Restart your computer.
Check Network Adapter Power Management Settings: The power management settings for your wireless adapter may, in some circumstances, be preventing it from functioning optimally.
- Open Device Manager.
- Expand "Network adapters."
- Right-click your wireless adapter, then select "Properties."
- Go to the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- Click "OK" and restart your computer.
Check Security Software: Your firewall or antivirus software might be blocking the connection. Temporarily disable your firewall or antivirus to see if it resolves the issue. If this works, you'll need to configure your security software settings to allow your wireless adapter to connect.
Reinstall the Network Adapter: The last resort that will always work is the reinstallation of the network adapter.
- Open Device Manager.
- Highlight Network Adapters.
- Find your network adapter.
- Right-click and choose uninstall.
- Click Action and choose to Scan for Hardware changes.
- Restart your computer.
Router Optimization: Maintaining a Healthy Network
While the focus has been on your Windows 10 device, the router plays a critical role. Consider these points:
Router Firmware: Ensure that your router's firmware is up-to-date. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements. Check your router manufacturer's website for instructions on updating the firmware.
Channel Selection: WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. In crowded environments, selecting a less-congested channel can improve performance and reduce interference. Access your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into a web browser) and experiment with different channels.
Wireless Mode: Ensure that your router is set to use a current wireless mode (e.g., 802.11ac or 802.11ax) for optimal speed and compatibility. Avoid outdated modes, like 802.11b/g, especially if your devices support newer standards.
Router Placement: The physical location of your router matters. Place it in an elevated, central location, away from walls, metal objects, and other electronics, which can interfere with the signal.
When All Else Fails: Seeking Outside Assistance
If you've exhausted these troubleshooting steps and your WiFi connection remains elusive, it's time to consider external assistance:
Contact Your ISP: Your internet service provider (ISP) can check for problems on their end, such as outages or service interruptions.
Seek Professional Help: A computer technician can diagnose hardware problems or more complex network issues that may be beyond your technical expertise.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Wireless Freedom
Having your WiFi vanish can be incredibly frustrating, but by systematically working through these troubleshooting steps, you can regain control of your connection. From the initial checks to more advanced techniques, this guide empowers you to diagnose and resolve these issues. Remember to be patient, methodical, and persistent. With a little effort and the right
