cara menyedot sinyal wifi di laptop
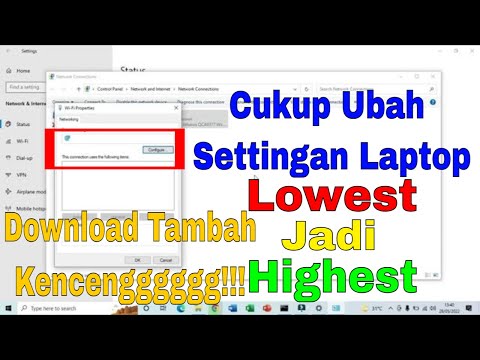
Title: Cara Mempercepat Koneksi Jaringan Wifi Di Laptop
Channel: Wira HK
Cara Mempercepat Koneksi Jaringan Wifi Di Laptop by Wira HK
cara menyedot sinyal wifi di laptop
Steal Your Neighbor's Wi-Fi: The Ultimate Laptop Guide
Cracking the Code: Your Laptop's Unofficial Wi-Fi Exploration Toolkit
Alright, friend, let's embark on a digital quest. Forget the stale technical jargon, we’re diving headfirst into how to get free internet. That's right, we're talking about understanding your laptop's Wi-Fi capabilities. Think of this as a friendly guide, a roadmap to navigating the sometimes-confusing world of wireless networks. Consequently, you're about to become a Wi-Fi whisperer.
The Wi-Fi Wilderness: Understanding the Landscape
First things first, let's set the scene. Imagine a vast digital wilderness. In this world, Wi-Fi signals are like invisible streams. Every router broadcasts these streams. Moreover, each stream is accessible, potentially. Understanding the signals is the first step to accessing them. Therefore, it’s crucial to grasp the concept of networks. Specifically, there are public networks and private networks. Public networks are open for everyone. However, private networks require a password. This is critical. You should know the difference.
Your Laptop: The Digital Explorer
Your laptop is your explorer’s kit. It’s your all-in-one tool for this adventure. Firstly, your laptop has a built-in Wi-Fi adapter. This adapter is like your explorer's antennae. Also, it receives Wi-Fi signals. Secondly, your operating system is your map. Windows or macOS, it shows you the available networks. Hence, your laptop sees a spectrum. As a result, it can identify all nearby Wi-Fi signals.
Decoding the Signals: Network Security Basics
However, not all signals are created equal. Some networks are locked down. Essentially, locked-down networks use encryption. Commonly, there are several encryption types. WEP is the oldest and weakest. WPA and WPA2 are more secure. Consequently, it’s significantly harder to crack these. Therefore, be mindful of the network you try to connect to. It is crucial to respect private networks.
Methods to Explore (Responsibly): The Open Network Approach
Now, let's talk about exploring networks. Specifically, the easiest way is to scan for open networks. These are networks without passwords. Generally, these are available for public use. For example, cafes, libraries, and public spaces. Consequently, you can connect instantly. In addition, remember to ensure you are using a secure website. As such, you protect your data.
Advanced Techniques (Use with Caution): Exploring with Permission
While we're at it, let's briefly touch on advanced techniques. Before we proceed, it's important to stress two things. First, obtaining permission is paramount. Second, accessing a private network without permission is unethical. Hence, we’ll talk about exploring these things indirectly. This usually involves penetration testing tools. But again, it is only for educational purposes. Moreover, there are many different tools available. These tools can help you understand the network.
Protecting Yourself: Security Practices
Moreover, internet security is essential. Whether you are on your Wi-Fi or someone else's. Therefore, we can offer some essential safety tips. Using a VPN is critical. This encrypts your traffic and masks your IP address. Moreover, having strong passwords is essential. You should also enable two-factor authentication on your important accounts.
The Ethical Considerations: Stay on the Right Side
Furthermore, let's remember the ethics. Respecting network boundaries is vital. Accessing someone's network without permission is wrong. It can lead to serious consequences. Focus on using your Wi-Fi for good. For example, streaming, research, or connecting with friends.
Troubleshooting: When Things Go Wrong
Unfortunately, problems can happen. So, what do you do when you can't connect? However, there is no need to panic. Start with the basics. Thus, check your Wi-Fi adapter. Ensure it is enabled. Also, try restarting your router. This can fix many issues. Sometimes, the problem is simple. The password may be incorrect. Finally, contact your internet service provider. They can often fix any issues.
Concluding Thoughts: Staying Connected
Finally, you should now have a better grasp of Wi-Fi networks. At the very least, you understand it better. In addition, you’re equipped with some basic knowledge. Always remember to explore responsibly. Therefore, your laptop becomes an even better resource. Go forth and explore the digital world!
HP 245 G5 Govt Laptop: Download WiFi Drivers NOW! (Solved!)Steal Your Neighbor's Wi-Fi: The Ultimate Laptop Guide
Hey there, tech adventurers! Ever found yourself staring at your laptop, the dreaded “no internet connection” message mocking you? We’ve all been there, right? That burning desire to binge-watch your favorite series, answer that crucial email, or just, you know, exist online. Now, while I strongly advocate for ethical internet use (and I'll say it again – don't be a jerk!), let's be real. Sometimes, the Wi-Fi gods aren't smiling. And sometimes, your neighbor's signal… whispers. So, without promoting anything illegal or immoral, consider this a tongue-in-cheek guide to navigating the potential world of your laptop's wireless capabilities. Let's dive into the ultimate guide to understanding Wi-Fi – and maybe, just maybe, a little peek at what's technically possible.
1. Decoding the Wi-Fi Whispers: A Beginner's Introduction
First things first: Wi-Fi. It's the invisible web that connects us, a digital playground we all take for granted. Think of it as a radio station, broadcasting information. Your laptop, your phone, your smart toaster – they're all little receivers, tuning into this station. But how does it all work? Understanding this basic principle is like learning the rules of the game before you play. Essentially, a router, like a friendly radio DJ, sends out signals. Your devices, the eager listeners, pick them up. It’s a two-way street, allowing you to send requests (like "load this webpage, please!") and receive information (like, well, the webpage!).
2. The Wi-Fi Detective: Identifying Networks Around You
Your laptop is a Wi-Fi detective in disguise. It's constantly scanning the airwaves, listening for those digital broadcasts. Most operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux) have built-in tools to show you available networks. It’s usually a simple icon in the system tray (that little area in the corner of your screen). Click it, and boom – a list of networks magically appears. Each one represents a different “radio station.”
3. The SSID Speaks: Deciphering Network Names
Every Wi-Fi network has an SSID (Service Set Identifier). Think of it as the network's name. You'll see things like "MyHomeWi-Fi," "Bob'sNetwork," or even something cryptic like "Linksys12345." The SSID is the first clue in the Wi-Fi mystery! Knowing the SSID is, in fact, the first step.
4. Security Protocols: The Fortress Around the Fortress
Now, here’s where things get interesting. Not all networks are created equal. Some are locked down tighter than Fort Knox, while others are… well, less secure. This is where security protocols come into play. The most common are:
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): Older, notoriously vulnerable. Think of it as a cardboard box – easy to break into.
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): A step up, but still shows its age. Consider it a wooden gate.
- WPA2: The current standard, reasonably secure. This is like having a steel door with a decent lock.
- WPA3: The newest and most secure, like a vault door.
The stronger the protocol, the tougher it is to “crack.” (Again, remember we're only hypothetically exploring the possibilities here.)
5. The Wi-Fi Password Puzzle: What’s the Hurdle?
The password is the key. It unlocks the network's door. Trying to guess it without permission is like trying to pick a lock! While the internet is awash with stories of individuals supposedly cracking passwords, this generally is a hard task.
6. Tools of the Trade (Hypothetically Speaking!): A Glimpse
Let's be clear: I'm not promoting anything illegal. But if you were to explore the hypothetical possibilities, there are tools that can (in theory) help you view the network's traffic. This might include things like packet sniffers, which monitor network traffic. And, yes, there are ways to potentially “break” a password, but it’s a complex, time-consuming, and ethically questionable endeavor. Remember, knowledge is power, but it also comes with responsibility.
7. The Importance of Ethical Consideration: A Moral Compass
Let's be clear: stealing Wi-Fi is against the law in many places and definitely not cool. It's like borrowing your neighbor's car without asking. Think of the potential consequences: legal trouble, strained relationships, and the bad karma that will haunt your digital life.
8. The Legal Landscape: Tread Carefully
Laws vary, but generally, accessing a network without permission is trespassing, at the very least. You could face fines, legal action, and a whole lot of unwanted attention. Do your research and always respect local laws, before anything else.
9. Protecting Your Own Wi-Fi: Fortifying the Fortress
Want to keep your network secure? Here's how:
- Strong Password: Use a complex password with uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Seriously, make it hard.
- Update Your Router Firmware: This patches security vulnerabilities.
- Enable WPA3: If your router and devices support it.
- Change Your Router's Default Password: Many routers come with default passwords that are easily found online.
- Monitor Your Network: Check which devices are connected.
10. The Open Network’s Warning: When Wi-Fi is Offered Freely
Free Wi-Fi hotspots may be tempting, but they often come with risks. They're often unsecured. Anyone on the same network can potentially see your data. Avoid doing sensitive activities (banking, shopping) on these networks.
11. Alternatives to Neighborly Wi-Fi (The Right Way!)
Before you even think about trying to "borrow" your neighbor's internet, consider these options:
- Talk to Your Neighbor: Maybe they'll be willing to share (for a small fee, perhaps?).
- Upgrade Your Internet Plan: Get a faster, more reliable connection.
- Mobile Hotspot: Use your phone as a Wi-Fi hotspot (if your plan allows it).
12. Troubleshooting Wi-Fi Woes: Getting Your Own Connection Working
If your own internet is down, try these common fixes:
- Restart Your Router and Modem: The classic "turn it off and on again" trick often works.
- Check Your Cables: Ensure everything is securely plugged in.
- Contact Your ISP: Your internet service provider can diagnose and fix issues.
13. The Cat-and-Mouse Game: Why It’s Often Futile
Even if you hypothetically managed to breach a network, it's a losing game. ISPs and network administrators are constantly updating their security. It is similar to trying to outrun a cheetah. The game goes on and on.
14. The Realities Of Slow or Unreliable Wi-Fi
Even if you could access a neighbor's network, chances are, it might not be a great experience. You could experience slow speeds, frequent dropouts, or even get cut off entirely if the neighbor suspects something. Is it worth the hassle and risk?
15. The Ultimate Takeaway: Respect and Responsibility
Here's the bottom line: Respect your neighbors, respect the law, and value your digital footprint. While technical curiosity is admirable, it shouldn’t come at the expense of others or your own reputation.
Conclusion:
So, there you have it – a deep dive into the world of Wi-Fi and the theoretical possibilities surrounding it. Remember, this guide is for informational purposes only and promotes ethical behavior. Stealing Wi-Fi is a no-go. Instead, focus on securing your own network, respecting your neighbors, and pursuing your internet adventures ethically. Now go forth and be a responsible digital citizen!
FAQs
1. Is it illegal to try and "crack" a Wi-Fi password?
Yes. In most jurisdictions, attempting to access a Wi-Fi network without permission is illegal. It could be considered trespassing, and you could face criminal charges.
2. What is the best way to secure my own Wi-Fi network?
Use a strong, unique password. Enable WPA3 if your devices support it. Keep your router's firmware updated. And change your router's default password.
3. What are the risks of using public Wi-Fi?
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured. This means that someone on the same network could potentially intercept your data, including passwords and personal information.
4. What should I do if my neighbor's Wi-Fi is slow?
First, check your device and internet connection. After that, if the issue persists, consider upgrading your internet plan or exploring different options, like a mobile hotspot.
5. What are the consequences of getting caught stealing Wi-Fi?
Consequences can range from a stern talking-to to fines, legal action, and damage to your reputation. It’s just not worth it.
- **
Cara Memperkuat Penangkapan Sinyal Wifi di Laptop

By Sobat OPS Cara Memperkuat Penangkapan Sinyal Wifi di Laptop by Sobat OPS
Cara menyedot semua jaringan wifi ke laptop

By Kadamsyah. .180954 Cara menyedot semua jaringan wifi ke laptop by Kadamsyah. .180954
laptop lemah menangkap sinyal wifi,begini solusinya
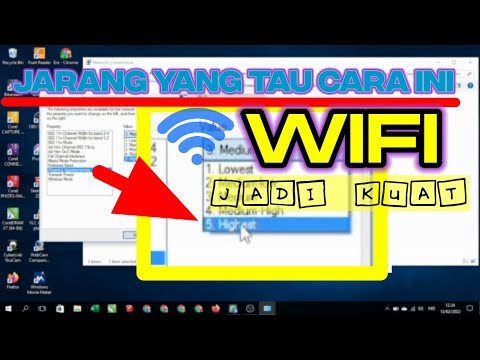
By Cemex Tutor laptop lemah menangkap sinyal wifi,begini solusinya by Cemex Tutor

Title: Cara mendapatkan kecepatan Internet Lebih Cepat dengan mengubah pengaturan sederhana
Channel: Liron Segev
Cara mendapatkan kecepatan Internet Lebih Cepat dengan mengubah pengaturan sederhana by Liron Segev
Wifi On Laptop Phone
Steal Your Neighbor's Wi-Fi: The Ultimate Laptop Guide
Navigating the digital landscape requires a secure internet connection. While the allure of free Wi-Fi is undeniable, accessing it unlawfully brings with it a spectrum of legal and ethical considerations. This guide is crafted to provide information. It will outline the technical aspects of Wi-Fi networks and the security measures in place. We are providing this information for educational purposes only. We want to emphasize the importance of respecting network boundaries and adhering to all applicable laws. This guide is designed to inform, not to condone or promote any illegal activity.
Understanding Wireless Networks: A Primer for the Modern User
Wireless networks, operating under the IEEE 802.11 standards, have become ubiquitous. These networks rely on radio waves to transmit data between devices and a central access point (often a router). Familiarity with the underlying principles of these networks is crucial for understanding their vulnerabilities and potential exploitation.
- Frequency Bands: Wireless networks operate on specific frequency bands, most commonly 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band offers broader coverage but is prone to interference. The 5 GHz band provides faster speeds and less congestion but has a shorter range. The choice of frequency band impacts network performance and the effectiveness of security protocols.
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): The SSID is the network's name, broadcast by the access point. It alerts devices to the presence of the network. While hiding the SSID can offer a modicum of obscurity, it's not a robust security measure. It can also lead to connectivity issues for devices.
- Channels: Within each frequency band, numerous channels allow devices to communicate. Routers automatically select a channel, or you can manually configure it. Selecting a less congested channel can help improve network performance.
- MAC Addresses: Each network interface card (NIC), whether wired or wireless, has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address. MAC addresses can be used to filter or monitor network traffic. This makes them a useful tool for network administrators, but also a point of focus for security enthusiasts.
- Wireless Standards (802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax): These standards define the protocols for wireless communication, including data rates, modulation techniques, and security features. Each subsequent standard has incrementally improved speeds and efficiency. The latest standard, Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax), offers the fastest speeds and uses the 6 GHz band.
Security Protocols: Fortress or Façade?
Securing a wireless network is crucial to prevent unauthorized access. Modern routers employ various security protocols, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): This is an older protocol, severely vulnerable to attack due to its weak encryption. It should never be used.
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): WPA provides better security than WEP, leveraging the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) for encryption. While an improvement over WEP, WPA is still susceptible to attacks and outdated.
- WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2): WPA2 uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for more robust encryption, making it significantly more secure than WEP or WPA. This is the standard for most modern networks.
- WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3): The latest and most secure protocol, WPA3, incorporates features like Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) to prevent dictionary attacks and enhanced security for open networks.
Tools of the Trade: Assessing Network Vulnerabilities (for informational purposes only)
Numerous tools are available for network assessment. These tools can aid in identifying vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
- Wireless Network Scanners: Software applications that scan for Wi-Fi networks, providing information about their SSIDs, channels, security protocols, and signal strength. Examples include InSSIDer, NetStumbler (Windows), and Wi-Fi Analyzer (Android).
- Packet Analyzers: Tools to capture and analyze network traffic, allowing users to examine the data flowing over a network, search for vulnerabilities, and identify information that can be useful for further investigation. Examples include Wireshark.
- Wireless Attack Frameworks: Comprehensive frameworks designed to test wireless network security. The best-known framework is Kali Linux, which includes a plethora of tools. These tools include:
- Aircrack-ng: A suite of tools for auditing wireless passwords that can be used for penetration testing and security assessment.
- Reaver: A tool to attack WPA/WPA2 networks by exploiting the WPS vulnerability.
- Password Cracking Tools: Software designed to crack passwords. These tools are used to test the strength of passwords that have been setup on a network.
The Legal Minefield: Navigating Ethical and Legal Considerations
Unauthorized access to a Wi-Fi network is against the law and often classified as computer theft. It can lead to significant penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and a criminal record. Beyond the legal ramifications, accessing a neighbor's Wi-Fi without permission raises ethical concerns. Respecting boundaries, both physical and digital, is essential for maintaining positive relationships.
- Terms of Service Violations: Most internet service providers (ISPs) have terms of service that explicitly prohibit unauthorized access to their networks. Violating these terms can lead to account termination and legal action.
- Data Privacy: When accessing someone else's network, you may have access to their personal data. This includes browsing history, emails, and other sensitive information.
- Cybercrime: Unauthorized access to a network could be used to commit cybercrimes, such as illegal downloads or online fraud.
Strengthening Your Own Network Security: A Proactive Approach
Securing your own Wi-Fi network is paramount to prevent unauthorized access. Implement these measures.
- Choose a Strong Password: Set a strong, complex password for your network, and the router control panel. Avoid using easily guessable information like your name, birthdate, or family member’s names.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: Ensure that your router uses WPA3. Upgrade your router if necessary.
- Change the Default SSID and Router Login: The default SSID and router login information are often publicly available, making your network vulnerable. Change these immediately after setting up your router.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup): WPS is a convenient feature that can be exploited, so it is best to disable it.
- Update Router Firmware: Keep your router's firmware up to date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor Network Activity: Regularly monitor your network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Use a Firewall: A firewall can help block unwanted traffic and protect your network from malicious attacks.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices.
Alternatives to Borrowing Wi-Fi: Legal and Ethical Solutions
If you need an internet connection and no public access is available, explore these alternatives.
- Public Wi-Fi: Many locations offer free Wi-Fi, including coffee shops, libraries, and public transportation hubs.
- Mobile Hotspot: Use your smartphone as a mobile hotspot.
- Mobile Data Plans: Subscribe to a mobile data plan.
- Ask for Permission: Always ask your neighbor before using their Wi-Fi.
Conclusion: Responsible Digital Citizenship
While the temptation of free Wi-Fi is understandable, the potential consequences of unauthorized access far outweigh any perceived benefits. Prioritize responsible digital citizenship. Build a secure network, and respect the boundaries of others. This approach helps maintain both your personal information security and community relations.
