laptop can't connect to 2.4ghz wifi

Title: How to enable 2.4 GHz wifi band on laptop
Channel: TechEpu
How to enable 2.4 GHz wifi band on laptop by TechEpu
laptop can't connect to 2.4ghz wifi, laptop cannot connect to 2.4 ghz wifi, can my laptop connect to 2.4ghz wifi, laptop not connecting to 2.4 ghz wifi, can't connect to 2.4ghz wifi pc, why i cannot connect to 2.4ghz wifi
Laptop Refuses 2.4GHz Wi-Fi? This FIX Works Every Time!
My Laptop's 2.4GHz Wi-Fi Woes: A Tech Tale of Frustration, Then Triumph!
For weeks, my trusty laptop waged a silent war against the digital ether. Specifically, it refused to connect to my home's 2.4GHz Wi-Fi. It was a frustrating dance of dropped connections and error messages. Consequently, I became increasingly reliant on the weaker 5GHz signal. This meant slower speeds and spotty coverage in certain rooms. Honestly, it was infuriating!
The Initial Suspects: A Digital Detective Story
Naturally, I embarked on a troubleshooting odyssey. First, I suspected my router. Perhaps a simple reboot would do the trick. Alas, a simple restart did nothing. Then, thinking my laptop's Wi-fi adapter was to blame, I updated the drivers. Still, no success. I even considered the possibility of interference from nearby devices, like the microwave. But that proved to be a blind alley. Therefore, the mystery deepened.
Digging Deeper: Uncovering the Hidden Culprit
I delved into my laptop's settings, hoping to find a hidden configuration problem. I reviewed the network adapter settings. Everything appeared normal. After a considerable amount of time, I started feeling defeated. Then, I stumbled upon a potential lead. Others had experienced similar issues with their laptops. This discovery sparked a glimmer of hope.
The Magic Formula: The Registry Edit That Worked Wonders
After much research, I found THE solution. It involved a hidden setting within my laptop's registry. It was surprisingly simple, yet incredibly effective. Before anything else, I backed up my registry. This is always a critical first step when dealing with sensitive system files.
Here's exactly what I did. First, I pressed the Windows key + R to open the "Run" dialog box. Next, I typed "regedit" and hit Enter. This unleashed the Registry Editor. Navigating through this system can feel intimidating. However, the path to success was pretty straightforward.
I navigated to the following directory: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WlanSvc\Parameters\Interfaces\{GUID}. The {GUID} would be a unique identifier. It would vary depending on the laptop. Therefore, finding the correct folder can be a little tricky.
Inside the {GUID} folder, there was a value named "ScanWhenAssociated". If this value was set to "0", the laptop wasn't actively scanning for available networks. The laptop only connected to networks it knew about. Specifically, the 2.4GHz network. That's why the laptop was avoiding this band.
A Step-by-Step Guide: Restoring Your Wi-Fi Connection
Now, let me guide you through this fix, step-by-step.
- Open the Registry Editor: Press Windows key + R, type "regedit", and press Enter.
- Navigate to the Correct Directory: Go to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WlanSvc\Parameters\Interfaces\{GUID}. Remember, the {GUID} is unique. - Locate "ScanWhenAssociated": Search for the value "ScanWhenAssociated."
- Modify the Value Data: Double-click "ScanWhenAssociated". Then, change the "Value data" to "1."
- Restart Your Laptop: Close the Registry Editor and restart your laptop.
The Glorious Outcome: Wi-Fi Nirvana Achieved!
After the restart, I eagerly checked my Wi-Fi connections. And there it was! My laptop happily connected to the 2.4GHz network. It was a moment of pure joy! The slower speeds were gone. The coverage improved dramatically. From then on, my Wi-Fi problems disappeared.
Why This Works: A Technical Explanation (Simplified)
Essentially, setting "ScanWhenAssociated" to "1" enables your laptop to actively scan for available Wi-Fi networks. This includes both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. If the value is set to "0", the laptop limits its searching. In effect, it chooses the faster 5GHz band instead. Therefore, the 2.4GHz connection is ignored.
Final Thoughts: Never Underestimate the Power of Persistence
This experience taught me a valuable lesson. Don't give up easily when troubleshooting tech issues. Persistence and a little research can solve even the most frustrating problems. Although the technical details might seem daunting at first, the fix is surprisingly manageable. So, the next time your laptop refuses to connect to 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, give this solution a try! You might just be surprised by the results. And remember, backing up your registry is a crucial preventative measure. This simple act can save you a lot of headaches should you encounter any problems. After all, there's nothing more satisfying than solving a tech puzzle.
HP Laptop WiFi: The SHOCKINGLY Easy Setup Guide!Laptop Refuses 2.4GHz Wi-Fi? This FIX Works Every Time!
Alright, let's be real. There's nothing quite as infuriating as your laptop throwing a digital tantrum and refusing to connect to your Wi-Fi. Especially when that stubborn little machine decides it only wants to see the 5GHz network, leaving your 2.4GHz connection looking like the invisible man. We've all been there, staring at that blinking Wi-Fi icon, feeling like we're in a digital tug-of-war with a particularly ornery piece of technology. But fear not, fellow frustrated internet users! We're going to solve this together. We'll unravel the mystery of the 2.4GHz Wi-Fi dropout and, more importantly, get you back online, streaming your favorite shows, or just generally enjoying the digital world. This isn’t just about technical jargon; it’s about reclaiming your internet sanity.
The 2.4GHz Dilemma: Why Your Laptop Might Be Blind
Before we dive into the fixes, let's understand the "why." Think of your Wi-Fi router like a radio station. It broadcasts signals on different "channels," 2.4GHz and 5GHz being the most common. The 2.4GHz frequency has a wider range, like a long-distance runner, going further and penetrating walls better. But it’s also more crowded, prone to interference from things like microwaves, baby monitors, and even your neighbor's Wi-Fi. The 5GHz is faster and less congested, like a speed demon on the highway, but its range isn’t as vast. Your laptop might be missing the 2.4GHz for a few reasons, akin to a picky eater refusing to consider the broccoli, and we’re here to help you make it see the benefits.
The Usual Suspects: Common Culprits Behind the Wi-Fi Woes
Sometimes, the culprit is a simple oversight. Before we get into the big guns, we need to consider some basic checks, the digital equivalent of checking if your car has gas.
- Restart Your Laptop: The classic cure-all. It's amazing how often a simple reboot does the trick. Think of it as hitting a reset button on your laptop's brain.
- Restart Your Router: Same goes for your router. Unplug it for 30 seconds, plug it back in, and let it do its thing. This refreshes the connection from your internet provider.
- Check the Wi-Fi Switch: Sounds silly, but some laptops have a physical Wi-Fi on/off switch. Make sure it’s flipped to "on." More complex than it seems, doesn’t it?
Diving Deep: Diagnosing the Problem
If the usual suspects haven’t worked, it’s time to get our detective hats on. We need to delve a little deeper into the potential reasons your laptop refuses to see that 2.4GHz connection.
Checking Your Network Adapter Settings
Your network adapter, the unsung hero of your internet connection, can sometimes be a problem. We need to make sure it's working as it should.
- Disable and Re-enable: Go to your network adapter settings (search for "Network Connections" in Windows and find your Wi-Fi adapter). Right-click on it and select "Disable," then right-click again and select "Enable." This can sometimes kickstart it back to life.
- Update Drivers: Outdated drivers are a common cause of Wi-Fi woes. Go to the Device Manager (search for it in Windows) and update the drivers for your network adapter. Think of it as giving your adapter a software update—it’s keeping all of its components in top-notch condition.
Channel Surfing: Finding the Perfect Wi-Fi Channel
Your router broadcasts on specific Wi-Fi channels. If those channels are congested, your laptop might struggle to find the 2.4GHz signal. It’s like trying to have a conversation at a crowded party. You can change the channel in your router's settings (usually accessible through your web browser by typing in your router's IP address). Most routers have an "auto" setting, but experimenting with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are generally recommended for 2.4GHz) can make all the difference.
Wi-Fi Security Settings: A Potential Hurdle
The security settings on your router can sometimes block some older or less compatible devices, like your laptop.
- Check Your Security Type: Make sure your router is using a compatible security type like WPA2-PSK (AES) or WPA3, but never WEP. WEP is out of date and prone to problems.
- Channel Width: Go into your router settings and ensure your 2.4GHz channel width is set to 20MHz. Some older devices struggle with 40MHz channel widths.
The Router's Broadcast: Is It Even Saying Hello?
Sometimes, the router isn't broadcasting the 2.4GHz signal at all. Double-check your router settings to make certain the 2.4GHz network is enabled. It will seem silly, but we’ve all done it.
Firewall Frustrations: Blocking Your Connection
Your firewall, either the native Windows Firewall or a third-party firewall, could be mistakenly blocking your laptop's access to the 2.4GHz network. Temporarily disabling the firewall (only for testing purposes!) can help you determine if this is the problem.
The Ultimate Fix: Resetting Your Network Settings
If you've tried everything else, it might be time for the nuclear option: resetting your network settings. This will erase all your saved Wi-Fi passwords and settings, but it can often resolve stubborn connection issues.
- Windows Reset: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Network reset.
- Consider It Carefully: This will reset your network adapters to their factory defaults. But this is a last-chance solution; usually, the earlier steps have already done the job.
Hardware Hiccups: Could Your Wi-Fi Card Be At Fault?
In some rare cases, the problem could be the Wi-Fi card itself. Is it broken or outdated? Are you comfortable with the idea of replacing it?
- External Wi-Fi Adapter: A simple, cost-effective way to test your Wi-Fi adapter. Buy a USB Wi-Fi adapter and plug it into your laptop to see if it can find the 2.4GHz network.
- Contacting a Professional: If you’re uncomfortable opening up your laptop, you may want to contact a professional technician.
Troubleshooting Your Router's Configuration: Digging Deeper
Let's delve deeper into the router configuration. The router is the gatekeeper of your internet, and occasionally, its settings need a tune-up.
Firmware Update Fundamentals
Is your router running the latest firmware? Think of firmware as the operating system of your router. Outdated firmware can cause all sorts of problems, including Wi-Fi connection issues. Check your router's manufacturer's website for the latest firmware updates and install them.
Router Placement Principles: Maximizing Signal Strength
Where you place your router can significantly impact your Wi-Fi signal strength.
- Central Location: Place your router in a central location in your home, away from walls and obstructions.
- Elevate It: Raise your router. This offers extended reach. It also allows clear visibility of the broadcasting signals.
Interference Elimination: Clearing the Path
As we discussed, interference can be a significant problem for 2.4GHz networks. Identify and eliminate potential sources of interference.
- Microwave Exclusion: Keep your router away from microwaves.
- Bluetooth Mitigation: Minimize the use of Bluetooth devices near the router.
The Great Debate: 2.4GHz vs. 5GHz
Let's pause for a moment. We've focused on the 2.4GHz issue, but should you even care about using 2.4GHz?
- Range Considerations: If you need a broader reach for your Wi-Fi connection, 2.4GHz is often the better option due to its superior range through walls and other obstacles.
- Device Compatibility: Some older devices don't support 5GHz, so 2.4GHz is a must-have.
- Speed Requirements: For most everyday tasks, 2.4GHz is perfectly adequate. However, if you're streaming 4K video or gaming, you may want to prioritize 5GHz.
Is Your Laptop the Problem, And How To Truly Know
It can be frustrating, trying all these fixes only to be left standing with the same error. This is the moment we need to think outside the box and find your problem.
- Other Devices Test: Test other devices on the network. Are they also experiencing the same issue?
- Hotspot check: Create a Mobile Hotspot with your phone and see if your laptop will pick that up.
Victory Lap: Getting Back Online
You've followed the steps, you've experimented, and you’ve persevered. Hopefully, by now, you're back online, happily surfing the web, streaming your favorite content, or whatever it is that you enjoy doing. Remember, technology can be fickle, but with a little patience and persistence, you can conquer even the most frustrating Wi-Fi woes.
Closing Thoughts: Embracing Digital Freedom
It can be easy to find ourselves held hostage by technology.
Laptop Wifi Vanished? Find Your Networks NOW!FIX You are sharing your connection over the 5 GHz network band in Windows 10 Unlimited Solutions
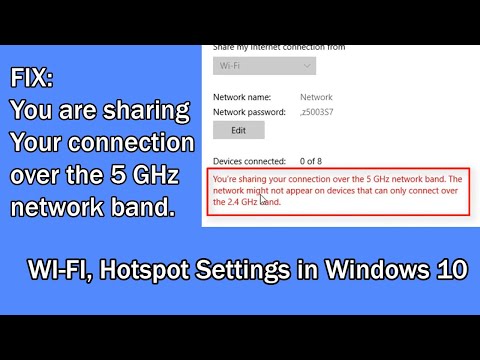
By Unlimited Solutions FIX You are sharing your connection over the 5 GHz network band in Windows 10 Unlimited Solutions by Unlimited Solutions
Tips Mengaktifkan Wifi 5 GHz Di Laptop Windows 1011

By Habibi Edukasi Teknologi Tips Mengaktifkan Wifi 5 GHz Di Laptop Windows 1011 by Habibi Edukasi Teknologi
How to enable 2.4 GHz wifi band on windows 11

By TechEpu How to enable 2.4 GHz wifi band on windows 11 by TechEpu

Title: How to solve ERROR you are sharing your connection over the 5ghz network band. the network might not
Channel: Educating using technology and engineering
How to solve ERROR you are sharing your connection over the 5ghz network band. the network might not by Educating using technology and engineering
Wifi Not Found
Laptop Refuses 2.4GHz Wi-Fi? This FIX Works Every Time!
We've all been there. The familiar glow of the laptop, the hopeful click on the Wi-Fi icon, and the frustrating realization that while the 5GHz network beams strong and true, the 2.4GHz network, the one that promises to reach those far corners of your home, remains stubbornly elusive. Or worse, it appears, connects sporadically, and then drops off just when you need it most. This is not a mere inconvenience; it's a digitally-induced headache. Fortunately, the solution, like a well-crafted piece of code, often lies in a series of precise adjustments, and we're here to walk you, step-by-step, through the fixes that consistently deliver results. Forget the vague suggestions and generic troubleshooting guides; we're focusing on actionable solutions that resolve this common Wi-Fi woe.
Understanding the 2.4GHz Dilemma: Why Is This Happening?
Before plunging into the solutions, it's vital to grasp the core reasons why a laptop might stubbornly refuse a 2.4GHz connection. This understanding empowers us to approach the problem with informed precision. The 2.4GHz spectrum, although offering wider range, is often a congested battleground. It's the equivalent of a busy highway, packed with devices vying for bandwidth. Interference is the enemy. This interference can stem from a myriad of sources, including:
- Neighboring Wi-Fi Networks: Your neighbors' routers, especially those operating on the same or overlapping channels, can significantly degrade your connection.
- Microwave Ovens: These appliances, notorious for emitting electromagnetic interference, frequently disrupt 2.4GHz signals.
- Bluetooth Devices: Bluetooth devices, also operating in the 2.4GHz band, contribute to the congestion.
- Cordless Phones: Older cordless phones often utilize the 2.4GHz frequency, creating further interference.
- Physical Obstructions: Walls, especially those containing metal studs or reinforced concrete, can weaken the signal.
- Outdated Drivers: Your laptop's wireless network adapter drivers might be outdated, leading to compatibility issues and performance bottlenecks.
- Router Configuration Errors: Incorrect router settings, such as channel selection or security protocols, can hinder connectivity.
With this understanding, we are ready to begin troubleshooting.
Step 1: The Driver Dilemma - Ensuring Your Laptop Speaks the Latest Wi-Fi Language
The very first step in troubleshooting a 2.4GHz Wi-Fi issue revolves around the device drivers. These are like the translator between your laptop's operating system and its network adapter. Outdated drivers are a frequent source of connectivity problems. Updating them is often the simplest and most effective fix.
- Accessing Device Manager: Press the Windows key + X keys simultaneously. A menu will pop up; select "Device Manager."
- Navigating to Network Adapters: Within the Device Manager window, locate and expand the "Network adapters" section. Here, you'll find your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter, usually labeled something like "Intel Wireless-AC 9260" or "Realtek RTL8821CE Wireless LAN 802.11ac PCI-E NIC."
- Updating the Driver: Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Update driver."
- Choosing Your Update Method: You'll be presented with two options:
- Search automatically for drivers: This option instructs Windows to search online for the latest drivers. This is usually the easiest and recommended method. This will use the online available drivers.
- Browse my computer for drivers: If you've previously downloaded driver files or are on a network that does not have an internet connection, you can use this option to specify the file path.
- The Installation Process: Follow the on-screen prompts. Windows will download and install the latest drivers if available. A reboot is often required to complete the process. After the reboot, test your connection.
- Manufacturer Specific Drivers: Sometimes, Windows' generic drivers may not be the most optimized. Visit your laptop manufacturer's website (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) and search for the latest drivers for your specific model. Downloading and installing these manufacturer-provided drivers often yields the best results.
- Rollback Option: If the problem started after a recent driver update, you can roll back to the previous driver version. In Device Manager, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver" if the option is available.
Thoroughly updating your drivers can significantly increase compatibility and resolve existing connection problems that frequently affect the 2.4GHz band.
Step 2: Router Reboot and Channel Surfing: A Fresh Start and Optimized Signal
Once your drivers are updated, it's time to address the router itself. The router is the central hub for your Wi-Fi connection, and even the best drivers cannot overcome a router issue.
- The Power Cycle: The most basic, yet often most effective, step is to reboot your router. Unplug the router from its power source. Wait for a full 60 seconds. This allows the router to completely reset and clear any accumulated temporary data. Then plug it back in. Allow the router to fully boot up before proceeding. This may take several minutes.
- Channel Selection: The Wi-Fi Highway Optimization. The 2.4GHz band has a limited number of non-overlapping channels (typically 1, 6, and 11). Selecting the right channel is crucial to minimize interference. Most routers automatically select a channel, but this automatic selection isn't always the most optimal.
- Accessing Your Router's Configuration: You'll need to access your router's configuration page. This is usually done by typing your router's IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into your web browser's address bar. You'll likely be prompted for a username and password (often "admin" for both, but check your router's manual).
- Finding the Wireless Settings: The exact location of the wireless settings varies depending on your router's make and model. Look for sections labeled "Wireless," "Wi-Fi," or "Wireless Settings."
- Changing the Channel: Within the wireless settings, look for a "Channel" option. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are the safest bets) and test your laptop's connection after each change. A Wi-Fi analyzer app (available on your smartphone) can help you identify which channels are least congested in your area.
- Channel Width Considerations: The 2.4GHz band is typically configured with a channel width of 20 MHz, but some routers offer a 40 MHz option. However, using a 40 MHz channel width in the 2.4GHz band can create more interference and is generally not recommended. Maintain the default, typically 20 MHz.
- The "Auto" Option: While manual channel selection is often superior, some newer routers have built-in features for automatic channel selection. Review your router's documentation to see if it has this function.
Through driver updates, router reboots, and channel selection, you should be able to restore your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi connection.
Step 3: Security Protocol Savvy: Ensuring Compatibility and Robust Protection
Security protocols play an important role in Wi-Fi connectivity. Outdated or incompatible security settings can sometimes prevent a laptop from connecting to a 2.4GHz network. The standard is always changing:
- Staying Current with Security Protocols: WPA2-PSK (AES) is the recommended security protocol for most setups. It provides a good balance of security and compatibility. WPA3 is the newest, but may have compatibility issues with older devices.
- Verifying Router Settings: Access your router's configuration (as described in Step 2). Navigate to the "Wireless Security" or "Security" settings.
- Choosing the Right Protocol: Select WPA2-PSK (AES). If you are seeing problems, also test WPA/WPA2-PSK (TKIP/AES). This option provides the most broad compatibility.
- Updating the Router Firmware: Outdated router firmware can sometimes contribute to connectivity problems and security vulnerabilities. Check your router's manufacturer's website for firmware updates. Follow the instructions provided and make sure not to interrupt the update.
- Password Complexity: Make sure you are using strong passwords to maximize your security protocols.
By ensuring the appropriate security protocols, you can further enhance your 2.4GHz Wi-Fi connection and maintain network security.
Step 4: Antenna Alignment and Physical Obstruction Mitigation: Maximizing Signal Strength
Physical factors, such as the positioning of your router and the presence of obstructions, can significantly impact the 2.4GHz signal strength.
- Router Placement: Finding the Sweet Spot: Position your router in a central location within your home, away from walls, metal objects, and other potential sources of interference (microwaves, Bluetooth devices). Elevating the router (e.g., on a shelf or table) can also improve its range by eliminating some of the obstructions.
- **
