my laptop is not detecting my wifi
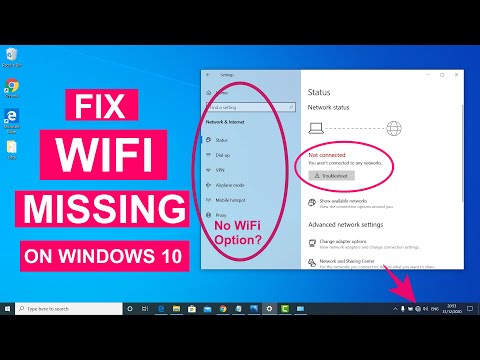
Title: Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
Channel: Sandeep Singh
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
my laptop is not detecting my wifi, my laptop is not detecting my wifi but detecting others, my laptop is not finding my wifi, my laptop is not seeing my wifi network, my laptop is not recognizing my wifi, my laptop can't detect wifi, my laptop is not detecting wifi adapter, why my laptop is not detecting my wi fi router, my laptop is not detecting any wifi network, my laptop is not detecting 5g wifi
Laptop WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW!
WiFi Woes? Your Laptop's Not-So-Secret Struggle – Solved!
Let's be honest, staring at that spinning wheel of doom while your laptop struggles to connect to WiFi is the digital equivalent of a slow news day. It’s frustrating, infuriating, and often, completely unnecessary. Your sleek, powerful laptop is suddenly as useful as a paperweight. Fear not, fellow tech traveler! Because we're diving headfirst into the vortex of wireless woes. We’ll emerge victorious, with your connection humming like a well-oiled machine.
The Phantom Signal: Diagnosing the WiFi Deficiency
Before you even think about throwing your laptop out the window (we've all been there), let’s play detective. The first step is understanding the enemy. Is your WiFi just plain gone? Or is it present, but tragically slow? Are you connected, but unable to load anything?
Consider this: is it only your laptop that's experiencing issues? If your other devices are enjoying blazingly fast internet, then it's time to zero in on your laptop. However, If everyone in your household is suffering, the problem may be with your internet service provider (ISP) or your router. Now that’s a different battle entirely.
Furthermore, Take a look at your WiFi signal strength. You can usually find this in the bottom right corner of your screen (Windows) or the top right (Mac). A strong signal with full bars is ideal. If you're seeing a weak signal or intermittent connection, then you're more likely experiencing these WiFi failures.
Router Reboot Ritual: The Cornerstone of Connectivity
It sounds cliché, but it's often the easiest and most effective fix. Your router, the unsung hero of your home network, can occasionally get a little… confused. So, unplug it from the power outlet. Wait a full 60 seconds. This allows your router to fully reset. Then, plug it back in and give it a few minutes to boot up.
After that, Test your connection again. Often, just this simple act can resolve many WiFi problems. If it doesn't work, don't be disheartened! We have several more tricks up our sleeves.
Driver Dilemmas: Keeping Your WiFi Card Updated
Your laptop's WiFi card is like the messenger pigeon of the digital age. The correct drivers are essential for this connection. These drivers are software programs that allow your laptop's operating system to communicate with your WiFi adapter. Outdated or corrupted drivers cause a multitude of issues.
So, let’s make sure your drivers are ship-shape. Windows users: Open Device Manager (search for it in the Start Menu). Locate "Network adapters." Expand this section. Right-click on your WiFi adapter (it might be listed as "Wireless Network Adapter" or something similar). Select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Follow the prompts.
On macOS: Apple usually handles driver updates automatically as part of its system updates. Make sure your operating system is up-to-date in System Preferences. Check for any pending updates.
Then, Restart your laptop after updating the drivers.
Channel Surfing: Minimizing Interference
WiFi operates on radio frequencies. These frequencies are divided into channels. Your router automatically selects a channel. But sometimes, it picks one already crowded. Other devices, even your neighbor's router, might be using the same channel. This causes interference, which results in a slower and more unreliable connection.
However, to fix this, access your router's settings. You can usually do this by typing your router's IP address into your web browser (it's often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1; check your router's documentation). Log in using the router's username and password.
Then, look for a setting related to "Wireless Channel" or "Channel Selection." Experiment with different channels. A common recommendation is to try channels 1, 6, and 11. After changing channels, save the settings and reboot your router.
The Distance Factor: Physical Obstacles and Signal Strength
Walls, particularly those made of concrete or brick, are notorious WiFi signal killers. The distance from your router matters too. The further you are, the weaker your signal. Therefore, positioning your router in a central and open location is crucial. Keep it elevated off the floor.
Furthermore, consider eliminating physical obstructions. Remove any items that might block the signal. This includes metal objects, large appliances, and even mirrors. Experiment by moving your laptop closer to the router. Notice if your connection improves.
Network Reset: A Final Reset
Sometimes, the issue lies in the network configurations stored on your laptop. A network reset can clear out any corrupted settings and restore your connection.
In Windows: Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Network reset. Click "Reset Now."
For Mac: You may need to remove the WiFi network from your preferred networks list. After this, Go to System Preferences > Network. Click “Advanced.” Locate your WiFi network and delete it. Then, reconnect to it using your password.
When to Call in the Cavalry: Seeking Professional Help
If none of the above steps work, it might be time to call in the experts. Contact your ISP to see if they can troubleshoot the problem. They may also have detected an outage in your area. Alternatively, take the laptop to a local computer repair shop. They can run more in-depth diagnostics and resolve any hardware issues.
However, don’t despair. In most cases, these easy fixes can solve common WiFi problems. You can enjoy fast, reliable internet access again. Your laptop WiFi nightmare? It's over! You’re back online, ready to conquer the digital world.
Laptop WiFi Hotspot: Why You're Offline & The SHOCKING Fix!Laptop WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW!
Hey there, fellow internet wanderers! Ever found yourself staring blankly at your laptop, the dreaded little WiFi icon displaying a big, fat "No Connection"? We've all been there. It’s like being trapped in a digital desert, craving the sweet oasis of the internet. Trust me, I've spent countless hours wrestling with this beast myself. But fear not, because we're going to conquer this laptop WiFi nightmare together! This isn’t just a list of basic fixes; this is a deep dive into the most common culprits and, more importantly, how to banish them from your life.
1. The WiFi Witch Hunt: Understanding Your Problem
Before you start smashing your laptop against the wall (tempting, I know!), let's understand the problem. Is it intermittent? Consistently terrible? Does it affect all your devices, or just the laptop? This initial assessment is crucial. Think of it as the first step in becoming a WiFi detective. Are you dealing with a simple cold, or a full-blown WiFi flu?
2. The "Are You Connected?" Checklist: Basic Troubleshoot
Okay, let's start with the basics. We all know the drill, but sometimes we overlook the obvious in our panic.
- Airplane Mode: Yes, I’ve done it. More than once. Double-check that Airplane Mode isn’t accidentally enabled. It's the equivalent of putting your laptop in solitary confinement.
- WiFi Switch: Make sure your laptop's WiFi switch (physical or software) is turned on. Sounds silly, I know, but… you know.
- Is it plugged in? No, I'm not kidding! Sometimes the tiniest things can make a huge difference.
- The Router Reboot Ritual: Unplug your router and modem, wait 30 seconds (torturous, I know!), and plug them back in. This is often the digital version of a reset button, and it's surprisingly effective.
3. Driver Drama: The Silent Culprit
Drivers are the unsung heroes of our digital lives. They're the software programs that allow your laptop's hardware to communicate effectively with the operating system. An outdated or corrupted WiFi driver can be a significant source of your WiFi woes.
- Driver Update Detective Work: Go to your Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar). Expand "Network adapters," and look for your WiFi adapter (it'll likely have "Wireless" or "WiFi" in the name). Right-click it, select "Update driver," and choose "Search automatically for drivers." Hopefully, your laptop will find new ones.
- Rollback to the Rescue: If a recent driver update caused the problem, you can roll back to a previous version. In the Device Manager, right-click your WiFi adapter, go to "Properties," and click on the "Driver" tab. If a "Roll Back Driver" option is available, use it.
4. The Signal Strength Saga: Where Are You Roaming?
The strength of your WiFi signal is critical. Think of it like a radio broadcast; the closer you are to the transmitter (your router), the clearer the signal. Distance, walls, and other electronic devices (like microwaves or Bluetooth speakers) can all degrade the signal.
- The Router Relocation: Experiment with moving your router to a more central, unobstructed location in your home. Higher is often better.
- Obstacle Course: Minimize the number of physical obstructions between your laptop and the router. Thick walls and metal objects are signal killers.
- Signal Strength Check: Use a WiFi analyzer app on your phone or laptop to check the signal strength. These apps can help you identify dead zones and optimize router placement.
5. Bandwidth Battles: 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz Showdown
Most modern routers offer two different WiFi bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band has a longer range, but it's often slower and more prone to interference. The 5 GHz band is faster and less crowded, but its range is shorter.
- Testing the Waters: Try connecting to both bands and see which one performs better in your specific situation.
- Channel Surfing: If you experience interference on the 2.4 GHz band, try changing the channel your router is broadcasting on. Most routers do this automatically, but sometimes manual adjustment is needed. This is especially important if you live in a densely populated area with many WiFi networks.
6. Firewall Frustrations: The Digital Gatekeeper
Your firewall, both the one built into your operating system and potentially any third-party firewall software, is designed to protect your computer. Sometimes, however, it can inadvertently block your WiFi connection.
- Temporary Test: Disable your firewall temporarily (for testing purposes only!). If your WiFi suddenly works, the firewall is the culprit.
- Whitelist Your Network Adapter: Configure your firewall to allow your WiFi adapter through. This usually involves adding an exception in your firewall settings.
- Software Conflicts: Consider if some recently installed software conflicts with your connection.
7. Malware Mayhem: The Silent Saboteur
Malware (malicious software) can wreak all sorts of havoc on your system, including interfering with your WiFi connection. It might be hogging bandwidth or actively trying to disrupt your network traffic.
- Scan for the Bad Guys: Run a full scan with your antivirus software. Make sure your antivirus definitions are up-to-date.
- The Malware Removal Dance: If malware is detected, follow your antivirus software's instructions for removal. Sometimes, a full system reinstall is the only way to fully remove a nasty piece of malware.
8. Router Configuration Chaos: Deeper Dive
Sometimes, the issue lies within your router's settings. This is where things get a little more technical, but often yields results.
- Check the Router Admin Page: Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing an IP address like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 into your web browser). You'll likely need a username and password, which are usually printed on the router's label or in its documentation.
- Security Protocol Check: Ensure your router is using a secure WiFi security protocol like WPA2 or WPA3. Older protocols like WEP are easily compromised.
- Channel Hopping: This may seem familiar from an earlier section, but it's worth revisiting. Wi-Fi channels can get overcrowded creating interruptions to your device.
9. The Hardware Hurdle: Is Your Adapter Faulty?
Sometimes, the problem isn't software-related at all. Your laptop's WiFi adapter itself might be faulty.
- External Adapter: If you have access to a USB WiFi adapter, test it on your laptop. If it works, it suggests the built-in adapter is the problem.
- Professional Help: If you suspect a hardware issue, consider taking your laptop to a computer repair shop. Replacing a WiFi adapter can sometimes be relatively inexpensive.
10. The Interference Inquisition: Identifying Digital Noise
Other electronic devices, particularly those operating on the 2.4 GHz band (like baby monitors, Bluetooth devices, and microwaves), can interfere with your WiFi signal.
- Device Audit: Identify potential sources of interference in your home.
- Test Removal: Try temporarily turning off or moving devices that could be causing interference.
- Channel Optimization: Experiment with different Wi-Fi channels.
11. The DNS Dilemma: Domain Name System Disruptions
Your Domain Name System (DNS) settings direct your computer to find the websites you request. If your DNS settings are messed up, you will not connect.
- Check your DNS: Google's DNS, for instance, is a freely used substitute (8.8.8.8 or 8.8.4.4)
- Clear cache: Often, if that is not the issue, a cache clearing is the next step.
12. Network Adapter Reset: A Troubleshooting Power-Up
Give your network adapter a full reset. This will refresh the adapter itself and bring it back to factory settings.
- Navigate through device manager: Go to the Device Manager (as before) and then right-click on your WiFi network adapter.
- Uninstall and then Reinstall: Uninstall the driver and then reinstall. This often helps!
13. Router Firmware Freshness: Keep it Updated!
Outdated firmware on your router can mean security issues. Firmware updates are like vaccine shots for your router.
- Check for Updates: In your router's admin web page, look for "firmware updates" or "system updates".
- Be Patient: Updates often take some time and the device must be online to do this.
14. Factory Reset Recon: A Path of Last Resort
If all else fails, a factory reset of your laptop might be necessary. This is like a digital exorcism, wiping your computer clean of all your data (so back up everything first!).
- Backup is Important: All your files should be backed up prior to this.
- Use your OS instructions: Each operating system has different instructions.
15. Seeking Professional Help: When to Admit Defeat
Sometimes, the problem is beyond our DIY capabilities.
- **
How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit

By Howtosolveit How to Fix WiFi Not Showing Up on Windows 10 - Howtosolveit by Howtosolveit
Windows laptop not connecting to Wi-Fi Method 1 shorts windows laptop wifi fix

By Tuto2Info Videos Windows laptop not connecting to Wi-Fi Method 1 shorts windows laptop wifi fix by Tuto2Info Videos
How To Fix wifi is not Connecting and Not Working on my laptop windows 10

By FIXsage How To Fix wifi is not Connecting and Not Working on my laptop windows 10 by FIXsage
Title: Fix Ethernet Connected But No Internet Access LAN Wired
Channel: ComeAndFixIT
Fix Ethernet Connected But No Internet Access LAN Wired by ComeAndFixIT
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
Laptop WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW!
We've all been there: that frustrating moment when your laptop refuses to connect to the internet, turning a productive workday or a relaxing evening into a tale of digital woe. A screaming "WiFi is not working" message can feel like a personal affront. But before you hurl technology out of the nearest window, take a deep breath. What seems like a catastrophic failure is often a fixable glitch. We're here to navigate you through the common culprits and deliver the solutions that will resurrect your internet connection and get you back online.
Diagnosis: Pinpointing the Source of Your WiFi Woes
Before diving into solutions, let’s establish a systematic approach to uncover the root of the problem. This diagnostic phase will prevent you from wasting time on ineffective fixes.
1. The Obvious: Check the Basics
Start with the simplest checks. Is the WiFi switch on your laptop activated? Many laptops have a physical switch, often located on the side or front, dedicated to enabling or disabling WiFi. Alternatively, look for a function key (usually one of the F keys, often with an antenna symbol) in conjunction with the "Fn" key.
Airplane Mode: Is Airplane Mode enabled? This setting, typically found in your system tray or settings menu, disables all wireless communication, including WiFi.
Router Reboot: A fundamental troubleshooting step is restarting your router. Unplug the router and modem (if separate) from the power source for at least 60 seconds. Plug them back in, modem first, then router, and wait for them to fully power on and establish a connection. The time required varies, but usually takes between one and five minutes.
2. The Laptop's Connection: Delving Deeper Within
If the basic checks reveal nothing, the next step is to examine your laptop's internal WiFi settings.
Check WiFi Status: Navigate to your system tray (bottom right of your screen, usually). Click on the WiFi icon. Are any networks listed? Can you see other available networks, even if you can't connect? If the icon displays a red X or a question mark, there’s definitely a problem.
Network Troubleshooter: Both Windows and macOS offer built-in network troubleshooters. Windows: right-click on the WiFi icon in the system tray and select "Troubleshoot problems." macOS: open "Network Preferences" in System Preferences and run diagnostics. These tools automatically identify and attempt to fix common connectivity issues.
Network Adapter Status: In Windows, search for "Device Manager" in the Start menu. Expand "Network adapters." Your WiFi adapter will be listed. If there’s a yellow exclamation mark next to the adapter, it indicates a driver issue. A red X indicates it is disabled. Double-click the adapter to view its status and troubleshoot.
3. External Factors: Your Internet Environment
The problem could lie beyond your laptop and your router.
Other Devices: Can other devices (phones, tablets, other laptops) connect to the WiFi? If they can, the problem is more likely specific to your laptop. If they can't, the issue is likely with your router or internet service provider.
Internet Service Provider (ISP) Outage: Occasionally, there might be an outage in your area. Check your ISP’s website or social media for announcements.
Solutions: Implementing the Fixes
With a good diagnosis in hand, it's time to implement solutions.
1. Driver-Related Issues: The Software Bridge
Driver issues are a frequent cause of WiFi problems.
Driver Updates: Obsolete, corrupted, or missing drivers can prevent WiFi from working. In the Device Manager (described above), right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will attempt to find and install the latest drivers.
Manual Driver Installation: If automatic updates fail, you can download drivers manually. Visit your laptop manufacturer's website (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) and navigate to the "Support" or "Drivers" section. Enter your specific laptop model number to find the correct drivers for your WiFi adapter; find the current driver, and download and install them.
Driver Rollback: If a recent driver update is the culprit, you can roll back to a previous version. In the Device Manager, right-click on the WiFi adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver."
Uninstall and Reinstall: Sometimes, a clean install is the best solution. In the Device Manager, right-click the WiFi adapter and select "Uninstall device." Reboot your laptop. Windows should automatically reinstall the driver. If not, use the manual driver installation method detailed above.
2. Network Configuration: Fine-Tuning Your Connection
Incorrect network settings can also trigger WiFi problems.
Forget and Reconnect: In your WiFi settings (accessed through the system tray icon), "forget" your current WiFi network. Then, reconnect, entering your password again. This forces the laptop to refresh the connection.
IP Configuration: Your laptop receives an IP address from the router. Occasionally, issues arise with this assignment. Resetting your IP configuration can resolve these issues.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Start menu) as an administrator. Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renewipconfig /flushdns
- macOS: Open Terminal (found in Applications > Utilities). Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
sudo ipconfig set en0 DHCP(Replace "en0" with your specific WiFi interface if needed, often Wi-Fi is "en0")sudo ipconfig renew en0sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder- You may be prompted for your administrator password.
- Windows: Open Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Start menu) as an administrator. Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
Network Reset (Windows 10/11): For a more comprehensive reset, Windows offers a network reset option. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset. This will reset all network adapters and settings to their default values.
DNS Servers: Your laptop uses DNS servers to translate website addresses into IP addresses. Occasionally, switching DNS servers can improve performance and resolve connectivity issues. You can use public DNS servers like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1). To change DNS servers:
- Windows: Go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings. Right-click on your WiFi adapter, select "Properties," and double-click on "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)." Select "Use the following DNS server addresses" and enter your preferred DNS servers.
- macOS: Go to System Preferences > Network. Select your WiFi connection, click "Advanced," go to the "DNS" tab, and add your preferred DNS servers.
3. Router Troubles: Addressing External Issues
Sometimes, the problem originates with your router.
Router Firmware: Ensure your router's firmware is up to date. Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues. Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 into your browser) and check for firmware updates.
Router Channel: WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. If your router is using a crowded channel, it can cause interference. Access your router's configuration page and explore the wireless settings. Look for an option to change the channel. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are often recommended).
Router Placement: The location of your router impacts WiFi signal strength. Place the router in a central location, away from obstructions like walls, metal objects, and other electronic devices. Elevate the router for improved signal distribution.
Router Reset (Again): If other troubleshooting steps have failed, try resetting your router to its factory settings. Locate the reset button (usually recessed, requiring a paperclip or similar tool) and hold it down for 15-30 seconds while the router is plugged in. Note: this will erase your router's settings, so you'll need to reconfigure it afterwards.
4. Security Software Interference: The Cybersecurity Factor
Sometimes, your security software can interfere with your WiFi connection.
Firewall: Your firewall might be blocking your laptop from connecting to the internet. Temporarily disable your firewall (e.g., Windows Firewall, or third-party firewall like McAfee or Norton) and see if that resolves the issue. If it does, you’ll need to add an exception for your WiFi network in your firewall’s settings.
Antivirus Software: Similarly, your antivirus software might be interfering. Temporarily disable your antivirus software (be careful while doing this, and only browse trusted websites) and see if the problem persists. If it resolves the issue, check your antivirus settings for any network-related features that might be causing the problem.
5. Hardware Issues: The Last Resorts
If software solutions fail, consider the possibility of hardware problems, particularly if the laptop is old.
- WiFi Adapter Malfunction: If all other troubleshooting steps have
