wifi wont work on laptop but works on phone
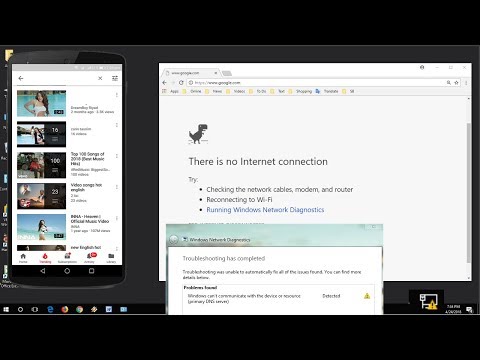
Title: Internet Coming In Phone But Not in PCLaptop Solved
Channel: MJ Tube
Internet Coming In Phone But Not in PCLaptop Solved by MJ Tube
wifi won t work on laptop but works on phone, wifi won t connect on laptop but will on phone, why is my wifi not working on my laptop but working on my phone, wifi not working in mobile but working in laptop, why is wifi working on laptop but not phone
Laptop WiFi Dead? Phone's Fine? This FIX Works!
Laptop WiFi Woes Got You Down? Here's the Rescue!
Okay, so your laptop's decided to go rogue. The WiFi icon is sulking, refusing to connect, while your phone’s happily streaming cat videos. Frustrating, isn't it? Let me tell you, I've been there – several times, in fact. Therefore, let's embark on a journey to get your laptop back online. Hopefully, these troubleshooting steps will work for you.
Is It Really the WiFi? Checking the Obvious First
Before we dive into the deep end, let's do a quick sanity check. First of all, is your WiFi switch actually turned on? It sounds silly, but it's a common issue. Check your keyboard; it often has a dedicated button or a combination. Secondly, reboot your laptop. Yes, a simple restart truly solves many tech problems. Additionally, make sure Airplane Mode is off. This setting can inadvertently kill your WiFi connection. Considering these simple fixes, we begin our journey.
Drivers, Drivers, Drivers: The Silent Culprit
Now, let's assume the basic checks failed. Often, the issue lies with your network adapter drivers. Drivers are essentially software that allows your laptop to "talk" to your WiFi card. Specifically, outdated or corrupted drivers can cause connection problems. Consequently, to fix this, we need to update them.
Here’s how:
- Access Device Manager: Type "Device Manager" into your Windows search bar and open it.
- Network Adapters: Expand the "Network adapters" section. You should see your WiFi adapter listed there (e.g., "Intel Wireless-AC 9260").
- Update Driver: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver."
- Automatic Search: Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will then try to find updated drivers.
- Manual Search (if needed): If updates aren’t found automatically, visit your laptop manufacturer's website. Download the latest drivers for your specific model. Then, choose "Browse my computer for drivers" in the Device Manager.
The Router's Role: A Potential Bottleneck
Sometimes, the problem isn’t your laptop at all. Instead, the router might be acting up. If other devices are struggling to connect, the router is the likely culprit. Furthermore, try these steps:
- Restart the Router: Unplug your router and modem. Wait for at least 30 seconds. Then, plug the modem back in first and allow it to boot up completely. Finally, plug the router back in. This simple reset often clears up minor glitches.
- Check Router Placement: Ensure your router is in a central location, free from obstructions. Walls and other electronic devices can interfere with the WiFi signal.
- Channel Interference: If you live in a densely populated area, your router might be experiencing interference from neighboring WiFi networks. Access your router’s settings (usually by typing its IP address into your browser). Look for the "Channel" setting. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, or 11 are often recommended).
Network Troubleshooting: Windows' Built-In Savior
Windows has a built-in troubleshooting tool that can be surprisingly effective. To run it:
- Settings: Go to your Windows settings.
- Network & Internet: Click on "Network & Internet."
- Troubleshooter: Select “Status” or "Troubleshoot." Windows will scan for issues and attempt to fix them.
Power Management: An Unexpected Sleepy Villain
Another potential cause: your power management settings. Your laptop might be configured to turn off the WiFi adapter to save battery life. This is a setting you can change.
- Device Manager (again): Go back to Device Manager and find your WiFi adapter.
- Properties: Right-click it and choose "Properties."
- Power Management Tab: Select the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the box: Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- Apply Changes: Click "OK."
Advanced Solutions: When All Else Fails
If all else has failed, here are a few more advanced steps:
- Network Reset: In Windows Settings, go to "Network & Internet," then "Advanced network settings." You should see a "Network reset" option. Be warned: This resets all your network settings, so you’ll need to re-enter your WiFi password.
- Check for Malware: Sometimes, malware can interfere with your network connection. Run a full system scan with your antivirus software.
- Reinstall Network Adapter: In Device Manager, right-click your WiFi adapter and choose "Uninstall device." Then, restart your computer. Windows should automatically reinstall the adapter.
The Final Word: Persistence Pays Off
Dealing with WiFi issues can be incredibly irritating. Nonetheless, don't give up! Carefully follow these troubleshooting steps, and you'll hopefully have your laptop connected in no time. Additionally, remember to stay patient, and take breaks if you need them. Good luck, and happy surfing!
HP Laptop WiFi Driver Nightmare? FIX IT NOW!Laptop WiFi Dead? Phone's Fine? This FIX Works!
Ever been staring at your laptop screen, a silent, mocking "No Internet" message glaring back at you while your phone, that little pocket-sized portal to the world, is happily buzzing with notifications? We've all been there. It's the digital equivalent of being stranded on a desert island, except instead of coconuts, you're craving cat videos and your email. It's frustrating, it's confusing, and frankly, it's enough to make you want to launch your laptop across the room. But before you succumb to the urge, take a deep breath. We're here to help. This isn’t just another generic troubleshooting guide; we’re diving deep into the mystery of why your laptop's Wi-Fi might be playing dead when your phone is perfectly fine, and – crucially – how to resurrect it. Let's get started!
1. The Great Wi-Fi Mystery: Why Your Laptop Is Sulking
So, what's the deal? Why does your trusty laptop decide to take a nap when your phone's Wi-Fi is working like a champ? Think of it like this: your phone and your laptop are communicating through the same language (Wi-Fi), but maybe, just maybe, your laptop has a bad translator. Several culprits could be at play, and we’ll be Sherlock Holmes (or maybe just a slightly tech-savvy friend) to figure them out.
2. The Usual Suspects: Quick & Easy Fixes First
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, let’s try the digital equivalent of checking if your car is plugged in. These are the easy wins, the things you can try even if you're not exactly a tech whiz.
- The Power Cycle: Yep, the old "turn it off and on again." Restarting your laptop is often the simplest solution. It clears out temporary glitches that might be messing with your Wi-Fi connection.
- The Router Reboot: Your laptop might be speaking the right language, but maybe the messenger is confused. Unplug your router for about 30 seconds, then plug it back in. Give it a couple of minutes to boot back up.
- Airplane Mode Frenzy: Toggling airplane mode on and off can sometimes kickstart your Wi-Fi adapter. It’s like giving your laptop a mental reset.
3. Driver Drama: Are Your Drivers the Problem?
If the quick fixes didn't work, it's time to suspect a driver malfunction. Think of drivers as tiny translators that allow your laptop to communicate with its hardware, including the Wi-Fi adapter. Corrupted or outdated drivers can be a major pain in the digital rear.
4. How to Update Your Wi-Fi Drivers (Without Tears)
Updating drivers sounds daunting, but trust us, it's easier than assembling IKEA furniture. Here's how:
- Windows: Search for "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar. Expand "Network adapters." Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter (it might be called something like "Wireless Network Adapter"). Select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will do its best to find the latest ones.
- Mac: Apple typically handles driver updates automatically through software updates. Check for updates in System Preferences > Software Update.
5. Signal Strength Struggles: Is Your Laptop Too Far Away?
This might seem obvious, but sometimes the simplest explanations are the best. Is your laptop far from the router? Wi-Fi signals, like invisible waves of delicious internet access, weaken over distance. Try moving your laptop closer to the router and see if that makes a difference. Think of it like trying to whisper to someone across a football field – it's just not going to work.
6. Channel Chaos: The Wi-Fi Traffic Jam
Your router broadcasts Wi-Fi on different channels, sort of like radio stations. If your neighbors are using the same channel, it can cause interference, creating a digital traffic jam. You can often log into your router's settings (usually by typing an IP address into your web browser, like 192.168.1.1) and change the Wi-Fi channel. Consult your router's manual for instructions.
7. Security Settings Shenanigans: WPA2 vs. WPA3
Have you recently upgraded your router? Sometimes, outdated security protocols can clash with your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter. Make sure both your router and laptop are using the latest security protocols, such as WPA3, for optimal compatibility.
8. The Blame Game: Is It Your Laptop's Fault?
Let's face it, sometimes the problem is your laptop. A hardware malfunction is possible, albeit less common. Has your laptop taken a tumble lately? Spilled a beverage on it? If you suspect a hardware issue, it might be time to consult a tech expert.
9. Software Conflicts: Does Security Software Mess Up Your Internet?
Sometimes, your security software, which is supposed to protect you, can inadvertently block your Wi-Fi connection. Temporarily disabling your antivirus or firewall can help determine if this is the cause. If so, you’ll need to configure your security software to allow Wi-Fi traffic.
10. Network Adapter Problems: The Hardware Heartbreak
In rare instances, your Wi-Fi adapter itself might be the culprit. It's like the antenna on your car radio breaking. You can try resetting your network adapter in the device manager. If this doesn’t work, you might need to replace the adapter.
11. The Wireless Adapter Switch: On or Off?
This sounds silly, but sometimes the simplest solution is the one we overlook. Ensure your laptop's wireless adapter is actually on. There's usually a physical switch on the side of your laptop or a function key combination (like Fn + F2) that enables or disables Wi-Fi.
12. Check Your Network Settings: IP Address Confusion
Your laptop receives an IP address from your router to connect to the internet. If the IP address is not correct, you cannot get online. Go to your network settings on your laptop and ensure your IP address is set to "Obtain an IP address automatically."
13. Test on Other Networks: Isolating the Issue
To see if it's your laptop or your Wi-Fi, try connecting to another Wi-Fi network, like a public hotspot or a friend's network. If your laptop connects fine to other networks, the problem is almost certainly with your home router or Wi-Fi.
14. Reset Network Settings: A Digital Clean Slate
In extreme cases, resetting your network settings to their default configuration can often resolve persistent Wi-Fi issues. Be warned, this will erase saved Wi-Fi passwords, so have them handy before you start.
15. When All Else Fails: Calling in the Pros
If you've tried everything, and your laptop's Wi-Fi still refuses to cooperate, it might be time to call in the professionals. A computer repair technician can diagnose and fix more complex hardware or software issues.
Conclusion: Your Laptop's Wi-Fi is Back!
And there you have it! We've explored the common culprits behind a dead laptop Wi-Fi connection while your phone merrily surfs. We've covered everything from the simple reboot to digging into the deep technical stuff. Remember, troubleshooting Wi-Fi problems is like a treasure hunt. You'll need to eliminate possible causes one by one, but with a little patience and some troubleshooting chops, you'll conquer your connectivity woes. Now go forth and reconnect!
FAQs
Q: My laptop can see my Wi-Fi network, but it can't connect. What's wrong?
A: This is a telltale sign of a problem with your password or the network itself. Double-check you're entering the right password. Also, try restarting your router.
Q: My laptop's Wi-Fi was working fine, but now it’s incredibly slow. What gives?
A: Slow Wi-Fi could be due to several factors: too many devices using the network, interference from other electronics, or the distance from the router. You can also try running a speed test from your laptop to diagnose if the problem is related to your internet plan.
Q: My laptop's Wi-Fi adapter is missing from Device Manager. Now what?
A: This could indicate a driver issue, a disabled adapter (check the switch), or a hardware problem. Try updating your drivers, enabling the adapter, or, if all else fails, getting professional help.
Q: My Wi-Fi works sometimes but not others. Why?
A: This intermittent issue is often related to interference, distance from the router, or a faulty router. Make sure you are close to your router.
Q: Is it my laptop's fault?
A: This is always a frustrating question. If it is not something we listed already, you may need to contact your internet service provider or a local tech expert.
- Principal Keywords: Laptop WiFi Fix Phone Fine
- SEO Headline: Laptop WiFi Dead? Fix It!
- Pathway: Laptop Fix
- Meta Summary: Laptop WiFi dead, phone working? Don't panic! This guide offers easy fixes to your laptop's Wi-Fi problems. Get back online now!
- Image
Wi-Fi connected on phone but not working on laptop Solved

By DD TechTV Wi-Fi connected on phone but not working on laptop Solved by DD TechTV
Fix Ethernet Connected But No Internet Access LAN Wired
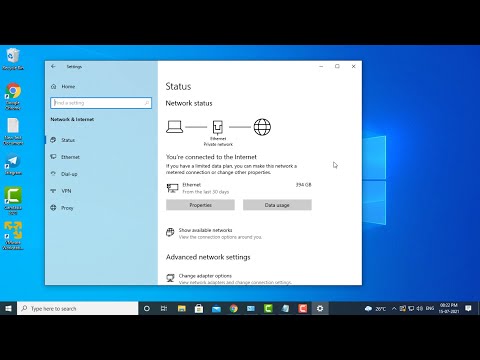
By ComeAndFixIT Fix Ethernet Connected But No Internet Access LAN Wired by ComeAndFixIT
Fix any Internet and Network Issues with this simple trick
By HowtoInsider Fix any Internet and Network Issues with this simple trick by HowtoInsider

Title: SOLVE Wi-Fi Not Connecting On Laptop But Working On Mobile Unidentified Network Problem Easily
Channel: Tuto2Info Videos
SOLVE Wi-Fi Not Connecting On Laptop But Working On Mobile Unidentified Network Problem Easily by Tuto2Info Videos
Change Wifi Settings
Let's begin.
Title: Demystifying the Art of Japanese Knotweed Eradication: A Comprehensive Guide for Homeowners
Japanese knotweed. The very words can instill a sense of dread in homeowners. This invasive species, Fallopia japonica, has rightfully earned its reputation as a formidable foe. Its aggressive growth, its tenacious root system (rhizomes), and its ability to colonize vast areas make eradication a complex undertaking. This guide, meticulously crafted for homeowners, offers a deep dive into the nuances of Japanese knotweed control, moving beyond superficial advice to provide actionable strategies for reclaiming your property.
Understanding the Enemy: The Biology and Behavior of Japanese Knotweed
Before engaging in any eradication efforts, a thorough understanding of the enemy is paramount. Japanese knotweed, a perennial plant, exhibits a remarkable ability to thrive in various environments. Its above-ground stems, which can reach heights of 7 to 10 feet, die back each winter, giving the illusion of dormancy. However, beneath the surface lies the true power of this plant: its extensive rhizome network.
These rhizomes, which can extend outwards as far as 20 meters from the main plant, are the primary means of propagation. Every fragment, even a small piece, can sprout into a new plant. This makes any disturbance, such as mowing or digging, a potential catalyst for further infestation. Furthermore, knotweed can regenerate from rhizome fragments that have been buried up to three meters deep. The plant's resilience extends to its ability to tolerate a wide range of soil conditions, including those that are nutrient-poor, disturbed, or even contaminated. It can also survive in areas with fluctuating water tables and varying levels of sunlight. This adaptability is a key factor in its success as an invasive species.
The plant's rapid growth rate is another significant challenge. New shoots emerge in the spring, quickly forming dense thickets that outcompete native vegetation for sunlight, water, and nutrients. This can lead to a significant loss of biodiversity and a disruption of the local ecosystem. The plant's ability to penetrate cracks in concrete, tarmac, and building foundations further contributes to its destructive potential.
Identifying the Culprit: Recognizing Japanese Knotweed and Avoiding Misidentification
Accurate identification is the first line of defense. Japanese knotweed can resemble other plants, particularly in its early stages of growth. Misidentification can lead to ineffective control methods and the potential spread of the plant.
The key characteristics of Japanese knotweed include:
- Stems: Bamboo-like, with reddish-purple speckles. They are hollow and jointed, resembling bamboo. These stems can grow rapidly, often several inches per day during peak growing season.
- Leaves: Broadly oval or heart-shaped, with a distinctive pointed tip. The leaves are typically 4 to 6 inches long and arranged alternately along the stem. They have a slightly crinkled appearance.
- Flowers: Small, creamy-white flowers that bloom in late summer or early autumn. They grow in clusters along the stems.
- Rhizomes: Thick, segmented, and reddish-brown. These underground stems are the plant's primary means of propagation.
It is crucial to distinguish Japanese knotweed from other similar-looking plants, such as bamboo (which has different leaf and stem characteristics), Himalayan balsam (which has pink flowers and seed pods that explode), and bindweed (which has distinctive trumpet-shaped flowers). If in doubt, consult with a local expert or utilize photographic resources to ensure accurate identification.
Control Strategies: A Multifaceted Approach to Japanese Knotweed Eradication
There is no single "magic bullet" for eradicating Japanese knotweed. Success requires a multifaceted approach that combines various control methods and a long-term commitment. The most common control strategies include:
- Chemical Control (Herbicide Application): This is often the most effective method, particularly for large infestations. Glyphosate and other herbicides specifically formulated for knotweed control are typically used. Repeated applications are often necessary, as the rhizomes can store energy and regrow even after initial treatments. Professional application is often recommended, as it ensures proper dosage and application techniques, minimizing the risk of environmental damage. The timing of application is crucial; it is most effective when the plant is actively growing and translocating nutrients to its rhizomes, typically in late summer or early autumn.
- Mechanical Control: This involves physically removing the plant, including its stems and rhizomes. This method is labor-intensive and requires meticulous attention to detail. Digging out the entire rhizome system is essential to prevent regrowth. Any fragments of the rhizomes left in the soil can regenerate, perpetuating the infestation. Regular mowing or cutting can weaken the plant over time, but it is unlikely to eradicate it completely. All plant material must be disposed of correctly, either by burning (where permitted) or by taking it to a licensed landfill.
- Combined Approaches (Integrated Pest Management): Combining chemical and mechanical control methods can often yield the best results. For instance, herbicide application can be followed by digging out any remaining plants or rhizome fragments. Regular monitoring is essential to detect and address any new growth.
- Biological Control: Currently, the primary biological control agent approved for use in the UK and some other regions is a sap-sucking psyllid, Aphalara itadori. This insect feeds on the plant's sap, weakening it over time. Biological control, while promising, is not a quick fix and can take several years to show significant results.
Best Practices for Effective Knotweed Eradication:
Successful knotweed eradication requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices:
- Professional Consultation: Consult with a qualified professional, such as an invasive species specialist or a certified herbicide applicator. They can assess the extent of the infestation, recommend the most effective control methods, and ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Permitting Considerations: Be aware of any local regulations regarding Japanese knotweed control. Some areas have specific requirements for herbicide application or waste disposal.
- Proper Disposal: Knotweed plant material must be disposed of in a way that prevents its spread. This typically involves burning (where permitted) or taking it to a licensed landfill. Composting is generally not recommended, as the rhizomes can survive the composting process.
- Long-Term Commitment: Knotweed eradication is a long-term process. Be prepared for repeated treatments and ongoing monitoring. It may take several years to completely eliminate the plant.
- Prevention: Prevent the introduction of knotweed to your property in the first place. Be vigilant in checking for it and avoid disturbing any areas where it might be present. Avoid purchasing contaminated soil or plants.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of all treatments, including dates, products used, and any observations about the plant's response. This information can be valuable in tracking your progress and making adjustments to your control strategy.
- Site Management: Implement proper site management practices to support the control methods. This includes ensuring good drainage, preventing soil erosion, and minimizing disturbance of the soil.
Navigating the Legal Landscape and Protecting Your Property:
Japanese knotweed is not just a nuisance; it can also have legal implications. Property values can be negatively impacted by the presence of knotweed. Moreover, there are legal liabilities associated with allowing knotweed to spread to neighboring properties.
- Duty of Care: Property owners are legally obligated to prevent the spread of Japanese knotweed. Failing to take reasonable steps to control it can result in legal action from neighboring property owners or local authorities.
- Property Disclosure: When selling a property, it is generally necessary to disclose the presence of Japanese knotweed. This disclosure can influence the property's value and may require the buyer to take corrective actions.
- Mortgage Implications: The presence of Japanese knotweed can potentially affect the ability to obtain a mortgage or home loan. Lenders may be hesitant to finance a property infested with knotweed due to the potential for damage and devaluation.
- Neighborly Relations: Communicate with your neighbors if you're dealing with Japanese knotweed that may spread to their properties. Cooperation can lead to more effective control strategies and avoid disputes.
The Path to a Knotweed-Free Property: A Summary and Call to Action
Eradicating Japanese knotweed is a challenging but achievable goal for homeowners. By understanding the plant's biology, accurately identifying it, employing a multifaceted control approach, and adhering to best practices, you can reclaim your property and prevent its spread. Remember that consistency, patience, and professional expertise are crucial. Regularly monitor the affected area and remain vigilant for any regrowth. With diligence and perseverance, you can successfully navigate the complexities of Japanese knotweed control and restore your property to its natural beauty. Consult a qualified professional for expert advice and assistance. Take action today to protect your property and secure your peace of mind.
